- About us»
- Net income calculator»
- Population aging»
-
-
- Unemployment structure in the Visegrad region
- Development in least developed regions
- Detailed statistics of least developed regions in Slovakia
- Statistics of the least developed regions in Slovakia
-
- Average wage
- Material need benefits
- Meal allowance
- Counties of Slovakia
- Inflation
- Living and Subsistence Minimum
- Unemployment of Czechia and Slovakia
- NACE Classification
-
- Life expectancy
- Gender differences
- Youth unemployment and NEET
- Minimum wage in EU
- Unemployment rates of different age groups
- Share of salaries on GDP
- Long term unemployment
- NEET
- Unemployment rate
- Percentage of employees ususally working at nights
- Employment rate
-
- Bratislava and surroundings
- Kopanice
- Danube river
- lower Vah river
- middle Vár river
- upper Nitra river
- lower Nitra river
- Mining cities
- Kysuce a Orava
- upper Vah river - Liptov
- Spiš cities
- upper Hron river
- Juhoslovenská kotlina
- Košice fold and Torysa river
- upper Zemplín
- lower Zemplín
- EU regions
- NUTS3 regions of Slovakia
- LAU1 dataset
-
-
- Projects and activities
- Inclusive growth»
- Good work
- Project SKRS
- Social system – reality and vision
- Library
-
- Education of unemployed
- Young unemployed not taking part in education
- Proposal to change the system of education funding
- News»
- Contact
Bamberg – DE241
EU regions: Germany > Bavaria > Upper Franconia > Bamberg
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Gross domestic product | ||
| GDP per capita in PPS of EU average | 2023 | 182 |
Bamberg slovensky: DE241
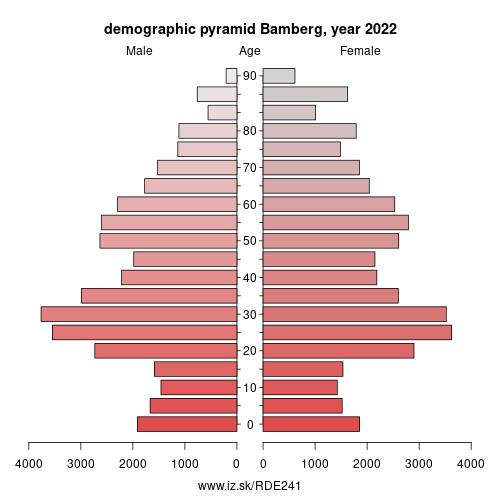
Demographics
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||
| number of inhabitants | 2025 | 77 150 |
| population density | 2023 | 1359 |
| old-age dependency ratio | 2025 | 30.1 |
From Wikipedia : Bamberg (, also US: , German: [ˈbambɛɐ̯k] (listen)) is a town in Upper Franconia, Germany, on the river Regnitz close to its confluence with the river Main. A large part of the town has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1993.
History
During the post-Roman centuries of Germanic migration and settlement, the region afterwards included in the Diocese of Bamberg was inhabited for the most part by Slavs. The town, first mentioned in 902, grew up by the castle Babenberch which gave its name to the Babenberg family. On their extinction it passed to the Saxon house. The area was Christianized chiefly by the monks of the Benedictine Fulda Abbey, and the land was under the spiritual authority of the Diocese of Würzburg.
In 1007, Holy Roman Emperor Henry II made Bamberg a family inheritance, the seat of a separate diocese. The Emperor's purpose in this was to make the Diocese of Würzburg less unwieldy in size and to give Christianity a firmer footing in the districts of Franconia, east of Bamberg. In 1008, after long negotiations with the Bishops of Würzburg and Eichstätt, who were to cede portions of their dioceses, the boundaries of the new diocese were defined, and Pope John XVIII granted the papal confirmation in the same year. Henry II ordered the building of a new cathedral, which was consecrated 6 May 1012.
Other: Upper Franconia, Coburg, Bayreuth, Forchheim District, Bamberg, Hof, Hof, Kulmbach, Kronach, Bamberg Rural District, Coburg, Lichtenfels, Bayreuth, Wunsiedel
Neighbours: Bamberg Rural District
Suggested citation: Michal Páleník: Europe and its regions in numbers - Bamberg – DE241, IZ Bratislava, retrieved from: https://www.iz.sk/PDE241, ISBN: 978-80-970204-9-1, DOI:10.5281/zenodo.10200164

 Share
Share Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter News
News