- About us»
- Net income calculator»
- Population aging»
-
-
- Unemployment structure in the Visegrad region
- Development in least developed regions
- Statistics of the least developed regions in Slovakia
- Detailed statistics of least developed regions in Slovakia
-
- Average wage
- Material need benefits
- Meal allowance
- Counties of Slovakia
- Inflation
- Living and Subsistence Minimum
- Unemployment of Czechia and Slovakia
- NACE Classification
-
- Life expectancy
- Gender differences
- Youth unemployment and NEET
- Minimum wage in EU
- Unemployment rates of different age groups
- Share of salaries on GDP
- Percentage of employees ususally working at nights
- Long term unemployment
- NEET
- Employment rate
- Unemployment rate
-
- Bratislava and surroundings
- Kopanice
- Danube river
- lower Vah river
- middle Vár river
- upper Nitra river
- lower Nitra river
- Mining cities
- Kysuce a Orava
- upper Vah river - Liptov
- Spiš cities
- upper Hron river
- Juhoslovenská kotlina
- Košice fold and Torysa river
- upper Zemplín
- lower Zemplín
- EU regions
- NUTS3 regions of Slovakia
- LAU1 dataset
-
-
- Projects and activities
- Inclusive growth»
- Good work
- Project SKRS
- Social system – reality and vision
-
- Education of unemployed
- Young unemployed not taking part in education
- Proposal to change the system of education funding
- Library
- News»
- Contact
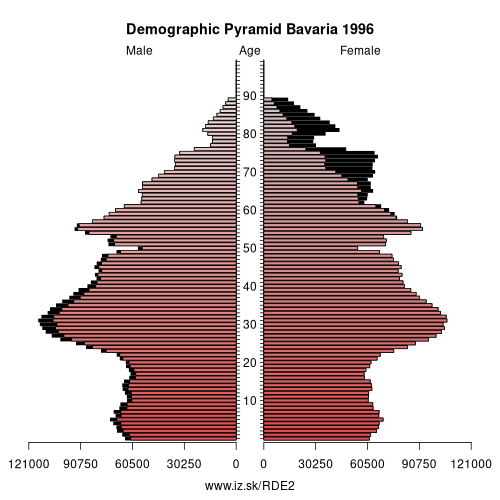
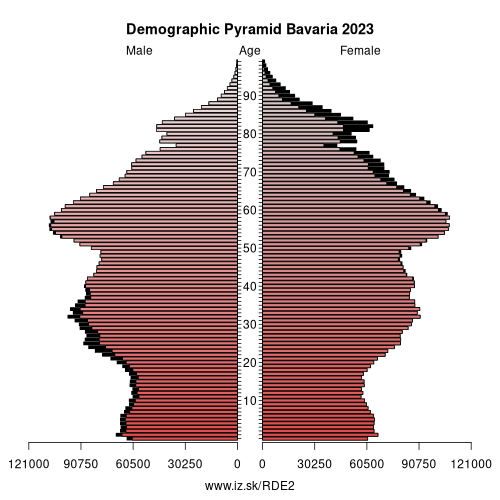
Bavaria – DE2
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Life long learning | ||
| life long learning participation | 2024 | 8.8 |
| Part time jobs and flexible employment | ||
| percentage of part time workers | 2024 | 30.61 |
| percentage of part time workers, men | 2024 | 11.09 |
| percentage of part time workers, women | 2024 | 52.67 |
| Gender differences | ||
| gender gap in employment rate | 2024 | 92.13 |
| gender gap in unemployment rate | 2024 | 96.15 |
| Graduates and young people | ||
| unemployment rate of youth with elementary education | 2024 | 7.3 |
| NEET | 2024 | 5 |
| Gross domestic product | ||
| GDP per capita in PPS of EU average | 2024 | 135 |
| Employment | ||
| employment rate | 2024 | 80.7 |
Bavaria slovensky: DE2
Subregions: Upper Bavaria, Lower Bavaria, Upper Palatinate, Upper Franconia, Middle Franconia, Lower Franconia, Swabia
Unemployment
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Unemployment | ||
| unemployment rate | 2024 | 2.7 |
| youth unemployment rate | 2024 | 5.1 |
| Long term unemployment | ||
| long term unemployment | 2024 | 0.6 |
| share of long term unemployed | 2024 | 24.1 |
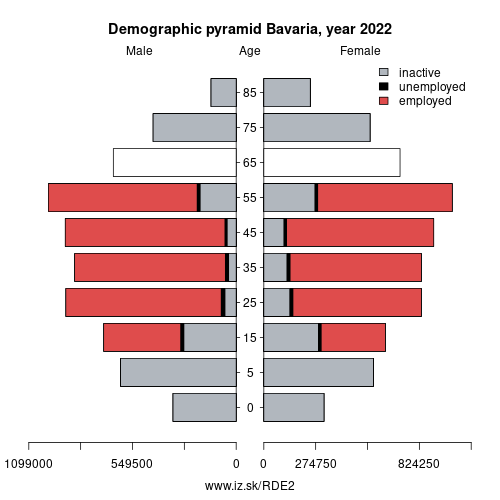
Demographics
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||
| number of inhabitants | 2025 | 13 248 928 |
| population density | 2024 | 189 |
| old-age dependency ratio | 2025 | 33.6 |
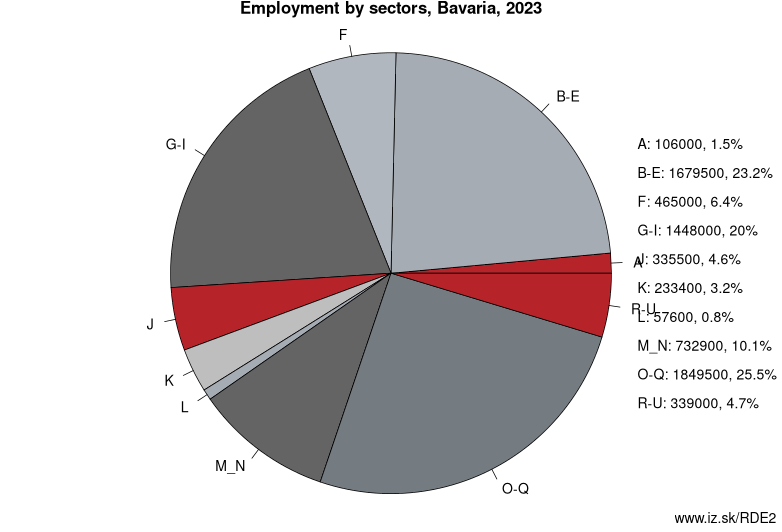
Employment by sectors, Bavaria
| NACE r2 | % | NACE r2 | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 93.7 | 1% | B-E | 1733.7 | 24% |
| F | 433.7 | 6% | G-I | 1419.3 | 20% |
| J | 331 | 5% | K | 224.8 | 3% |
| L | 61 | 1% | M_N | 680.6 | 10% |
| O-Q | 1830.9 | 26% | R-U | 341 | 5% |
| TOTAL | 7149.6 | 100% |
Data for the period year 2024. Source of the data is Eurostat, table [lfst_r_lfe2en2].
From Wikipedia :
Bavaria (; German and Bavarian: Bayern [ˈbaɪɐn]), officially the Free State of Bavaria (German and Bavarian: Freistaat Bayern [ˈfʁaɪʃtaːt ˈbaɪɐn]), is a landlocked federal state of Germany, occupying its southeastern corner. With an area of 70,550.19 square kilometres (27,200 sq mi), Bavaria is the largest German state by land area comprising roughly a fifth of the total land area of Germany. With 13 million inhabitants, it is Germany's second-most-populous state after North Rhine-Westphalia. Bavaria's main cities are Munich (its capital and largest city and also the third largest city in Germany), Nuremberg and Augsburg.The history of Bavaria includes its earliest settlement by Iron Age Celtic tribes, followed by the conquests of the Roman Empire in the 1st century BC, when the territory was incorporated into the provinces of Raetia and Noricum. It became a stem duchy in the 6th century AD following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. It was later incorporated into the Holy Roman Empire, became an independent kingdom, joined the Prussian-led German Empire in 1871 while retaining its title of kingdom, and finally became a state of the Federal Republic of Germany in 1949.
The Duchy of Bavaria dates back to the year 555. In the 17th century AD, the Duke of Bavaria became a Prince-elector of the Holy Roman Empire. The Kingdom of Bavaria existed from 1806 to 1918, when Bavaria became a republic. In 1946, the Free State of Bavaria reorganized itself on democratic lines after the Second World War.
Other: Germany, Saarland, Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, Baden-Württemberg, Hamburg, Berlin, North Rhine-Westphalia, Hesse, Bavaria, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Schleswig-Holstein, Brandenburg, Bremen, Rhineland-Palatinate, Thuringia, Lower Saxony
Neighbours: Saxony, Baden-Württemberg, Western Austria, Thuringia, Hesse, Czech Republic, SCHWEIZ/SUISSE/SVIZZERA
Subregions: Upper Bavaria, Lower Bavaria, Upper Palatinate, Upper Franconia, Middle Franconia, Lower Franconia, Swabia
Suggested citation: Michal Páleník: Europe and its regions in numbers - Bavaria – DE2, IZ Bratislava, retrieved from: https://www.iz.sk/PDE2, ISBN: 978-80-970204-9-1, DOI:10.5281/zenodo.10200164

 Share
Share Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter News
News