- About us»
- Net income calculator»
- Population aging»
-
-
- Unemployment structure in the Visegrad region
- Development in least developed regions
- Detailed statistics of least developed regions in Slovakia
- Statistics of the least developed regions in Slovakia
-
- Average wage
- Material need benefits
- Meal allowance
- Counties of Slovakia
- Inflation
- Living and Subsistence Minimum
- Unemployment of Czechia and Slovakia
- NACE Classification
-
- Life expectancy
- Gender differences
- Youth unemployment and NEET
- Minimum wage in EU
- Unemployment rates of different age groups
- Share of salaries on GDP
- Long term unemployment
- Percentage of employees ususally working at nights
- NEET
- Unemployment rate
- Employment rate
-
- Bratislava and surroundings
- Kopanice
- Danube river
- lower Vah river
- middle Vár river
- upper Nitra river
- lower Nitra river
- Mining cities
- Kysuce a Orava
- upper Vah river - Liptov
- Spiš cities
- upper Hron river
- Juhoslovenská kotlina
- Košice fold and Torysa river
- upper Zemplín
- lower Zemplín
- EU regions
- NUTS3 regions of Slovakia
- LAU1 dataset
-
-
- Projects and activities
- Inclusive growth»
- Good work
- Project SKRS
- Social system – reality and vision
- Library
-
- Education of unemployed
- Young unemployed not taking part in education
- Proposal to change the system of education funding
- News»
- Contact
Rhineland-Palatinate – DEB
EU regions: Germany > Rhineland-Palatinate
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Life long learning | ||
| life long learning participation | 2024 | 9.4 |
| Part time jobs and flexible employment | ||
| percentage of part time workers | 2024 | 31.8 |
| percentage of part time workers, men | 2024 | 11.93 |
| percentage of part time workers, women | 2024 | 54.38 |
| Gender differences | ||
| gender gap in employment rate | 2024 | 91.79 |
| gender gap in unemployment rate | 2024 | 74.29 |
| Graduates and young people | ||
| unemployment rate of youth with elementary education | 2019 | 9.1 |
| NEET | 2024 | 7.7 |
| Gross domestic product | ||
| GDP per capita in PPS of EU average | 2024 | 100 |
| Employment | ||
| employment rate | 2024 | 78.3 |
Rhineland-Palatinate slovensky: DEB
Subregions: Koblenz Government Region, Trier Government Region, Rheinhessen-Pfalz
Unemployment
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Unemployment | ||
| unemployment rate | 2024 | 3.2 |
| youth unemployment rate | 2024 | 7 |
| Long term unemployment | ||
| long term unemployment | 2024 | 0.7 |
| share of long term unemployed | 2024 | 23.8 |
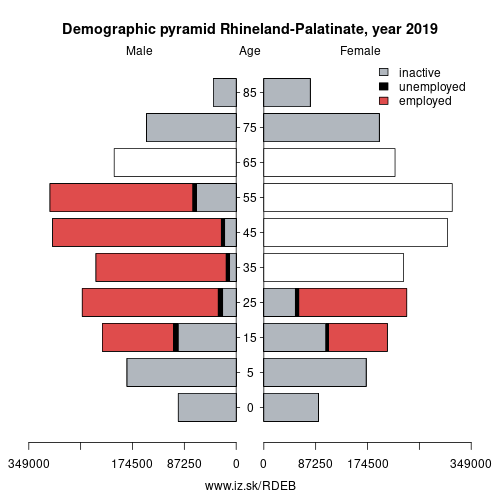
Demographics
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||
| number of inhabitants | 2025 | 4 129 569 |
| population density | 2024 | 209.3 |
| old-age dependency ratio | 2025 | 37.1 |
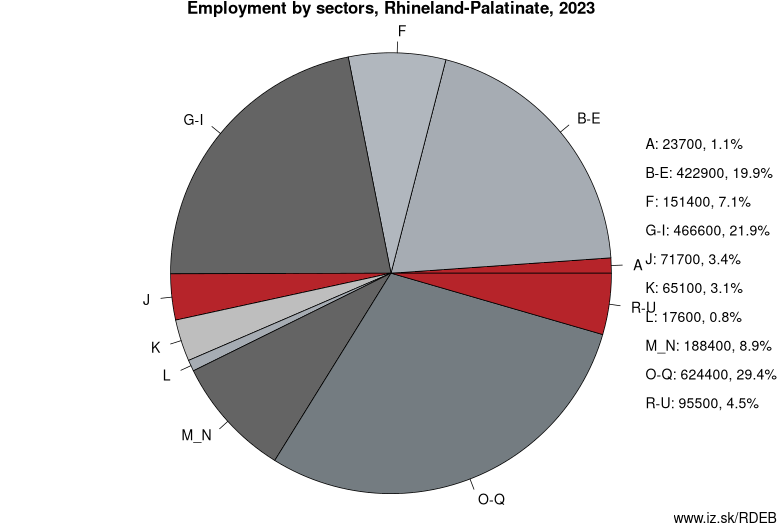
Employment by sectors, Rhineland-Palatinate
| NACE r2 | % | NACE r2 | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 25.5 | 1% | B-E | 408.9 | 19% |
| F | 151.6 | 7% | G-I | 459.7 | 22% |
| J | 81.3 | 4% | K | 58.6 | 3% |
| L | 16.2 | 1% | M_N | 188.1 | 9% |
| O-Q | 634.7 | 30% | R-U | 96 | 5% |
| TOTAL | 2120.6 | 100% |
Data for the period year 2024. Source of the data is Eurostat, table [lfst_r_lfe2en2].
From Wikipedia : Rhineland-Palatinate (German: Rheinland-Pfalz, pronounced [ˈʁaɪ̯nlant ˈp͡falt͡s]) is a state of Germany.
Rhineland-Palatinate is located in western Germany covering an area of 19,846 km2 (7,663 sq mi) and a population of 4.05 million inhabitants, the seventh-most populous German state. Mainz is the state capital and largest city, while other major cities include Ludwigshafen am Rhein, Koblenz, Trier, Kaiserslautern, and Worms. Rhineland-Palatinate is surrounded by the states of North Rhine-Westphalia, Saarland, Baden-Württemberg, and Hesse. It also borders three foreign countries: France, Luxembourg, and Belgium.
Rhineland-Palatinate was established in 1946 after World War II from territory of the historically separate regions of the Free State of Prussia, People's State of Hesse, and Bavaria, by the French military administration in Allied-occupied Germany. Rhineland-Palatinate became part of the Federal Republic of Germany in 1949, and shared the country's only border with the Saar Protectorate until it was returned to German control in 1957. Rhineland-Palatinate has since developed its own identity built on its natural and cultural heritage, including the extensive Palatinate winegrowing region, its picturesque landscapes, and many castles and palaces.
History
The state of Rhineland-Palatinate was founded shortly after the Second World War on 30 August 1946. It was formed mainly from the southern part of the Prussian Rhine Province (the Regierungsbezirke of Koblenz and Trier), from Rhenish Hesse, from the western part of Nassau and the Bavarian Rhenish Palatinate minus the county of Saarpfalz. The Joint German-Luxembourg Sovereign Region (Gemeinschaftliches deutsch-luxemburgisches Hoheitsgebiet) is the only unincorporated area of the state of Rhineland-Palatinate.
Other: Germany, Saarland, Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, Baden-Württemberg, Hamburg, Berlin, North Rhine-Westphalia, Hesse, Bavaria, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Schleswig-Holstein, Brandenburg, Bremen, Rhineland-Palatinate, Thuringia, Lower Saxony
Neighbours: Saarland, Grand Est, Baden-Württemberg, North Rhine-Westphalia, Luxembourg, Hesse, Wallonia
Subregions: Koblenz Government Region, Trier Government Region, Rheinhessen-Pfalz
Suggested citation: Michal Páleník: Europe and its regions in numbers - Rhineland-Palatinate – DEB, IZ Bratislava, retrieved from: https://www.iz.sk/PDEB, ISBN: 978-80-970204-9-1, DOI:10.5281/zenodo.10200164

 Share
Share Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter News
News