- About us»
- Net income calculator»
- Population aging»
-
-
- Unemployment structure in the Visegrad region
- Development in least developed regions
- Detailed statistics of least developed regions in Slovakia
- Statistics of the least developed regions in Slovakia
-
- Average wage
- Material need benefits
- Meal allowance
- Counties of Slovakia
- Inflation
- Living and Subsistence Minimum
- Unemployment of Czechia and Slovakia
- NACE Classification
-
- Life expectancy
- Gender differences
- Youth unemployment and NEET
- Minimum wage in EU
- Unemployment rates of different age groups
- Share of salaries on GDP
- Unemployment rate
- Percentage of employees ususally working at nights
- Employment rate
- NEET
- Long term unemployment
-
- Bratislava and surroundings
- Kopanice
- Danube river
- lower Vah river
- middle Vár river
- upper Nitra river
- lower Nitra river
- Mining cities
- Kysuce a Orava
- upper Vah river - Liptov
- Spiš cities
- upper Hron river
- Juhoslovenská kotlina
- Košice fold and Torysa river
- upper Zemplín
- lower Zemplín
- EU regions
- NUTS3 regions of Slovakia
- LAU1 dataset
-
-
- Projects and activities
- Inclusive growth»
- Good work
- Project SKRS
- Social system – reality and vision
- Library
-
- Education of unemployed
- Young unemployed not taking part in education
- Proposal to change the system of education funding
- News»
- Contact
Baden-Württemberg – DE1
EU regions: Germany > Baden-Württemberg
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Life long learning | ||
| life long learning participation | 2024 | 9.7 |
| Part time jobs and flexible employment | ||
| percentage of part time workers | 2024 | 31.73 |
| percentage of part time workers, men | 2024 | 12.34 |
| percentage of part time workers, women | 2024 | 53.91 |
| Gender differences | ||
| gender gap in employment rate | 2024 | 91.47 |
| gender gap in unemployment rate | 2024 | 87.5 |
| Graduates and young people | ||
| unemployment rate of youth with elementary education | 2024 | 9.6 |
| NEET | 2024 | 6.9 |
| Gross domestic product | ||
| GDP per capita in PPS of EU average | 2024 | 131 |
| Employment | ||
| employment rate | 2024 | 79.7 |
Baden-Württemberg slovensky: DE1
Subregions: Stuttgart Government Region, Karlsruhe Government Region, Freiburg Government Region, Tübingen Government Region
Unemployment
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Unemployment | ||
| unemployment rate | 2024 | 3.1 |
| youth unemployment rate | 2024 | 6.7 |
| Long term unemployment | ||
| long term unemployment | 2024 | 0.6 |
| share of long term unemployed | 2024 | 19.5 |
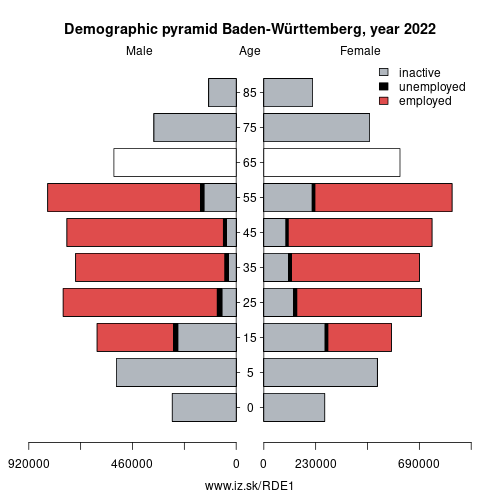
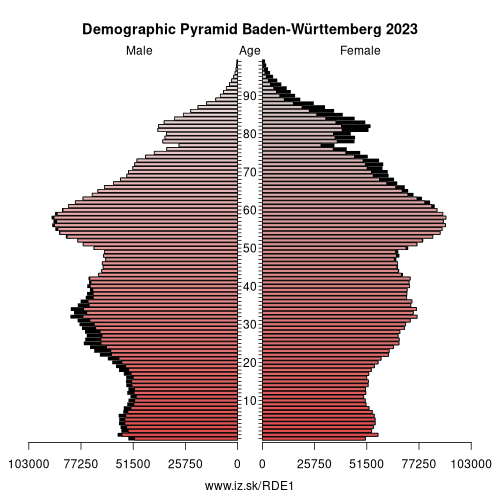
Demographics
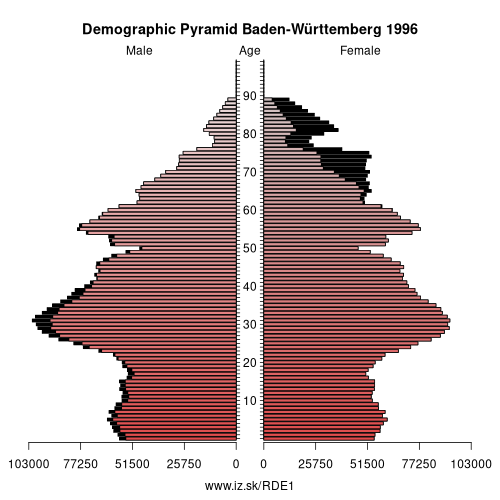
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||
| number of inhabitants | 2025 | 11 245 898 |
| population density | 2023 | 316.8 |
| old-age dependency ratio | 2025 | 33.6 |
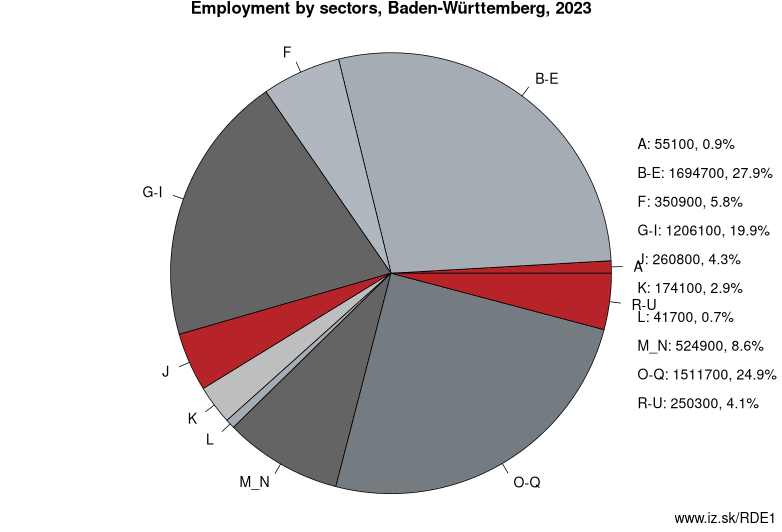
Employment by sectors, Baden-Württemberg
| NACE r2 | % | NACE r2 | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 45.7 | 1% | B-E | 1645 | 27% |
| F | 362.4 | 6% | G-I | 1182.8 | 20% |
| J | 254.1 | 4% | K | 170.1 | 3% |
| L | 39.6 | 1% | M_N | 536 | 9% |
| O-Q | 1554.1 | 26% | R-U | 250.8 | 4% |
| TOTAL | 6040.5 | 100% |
Data for the period year 2024. Source of the data is Eurostat, table [lfst_r_lfe2en2].
From Wikipedia : Baden-Württemberg (, German: [ˌbaːdn̩ ˈvʏʁtəmbɛʁk] (listen)) is a state in southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the border with France. It is Germany’s third-largest state, with an area of 35,751 km2 (13,804 sq mi) and 11 million inhabitants. Baden-Württemberg is a parliamentary republic and partly sovereign, federated state which was formed in 1952 by a merger of the states of Württemberg-Baden, Baden and Württemberg-Hohenzollern. The largest city in Baden-Württemberg is the state capital of Stuttgart, followed by Karlsruhe and Mannheim. Other cities are Freiburg im Breisgau, Heidelberg, Heilbronn, Pforzheim, Reutlingen and Ulm.
The sobriquet Ländle ("little province" in the local Swabian and Alemannic German dialects) is sometimes used as a synonym for Baden-Württemberg.
History
Baden-Württemberg is formed from the historical territories of Baden, Prussian Hohenzollern, and Württemberg, and also parts of Swabia.
In 100 AD, the Roman Empire invaded and occupied Württemberg, constructing a limes (fortified boundary zone) along its northern borders. Over the course of the third century AD, the Alemanni forced the Romans to retreat west beyond the Rhine and Danube rivers. In 496 AD the Alemanni were defeated by a Frankish invasion led by Clovis I.
The Holy Roman Empire was later established. The majority of people in this region continued to be Roman Catholics, even after the Protestant Reformation influenced populations in northern Germany. In the late-nineteenth and early-twentieth centuries, numerous people emigrated from this mostly rural area to the United States for economic reasons.
Other: Germany, Saarland, Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, Baden-Württemberg, Hamburg, Berlin, North Rhine-Westphalia, Hesse, Bavaria, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Schleswig-Holstein, Brandenburg, Bremen, Rhineland-Palatinate, Thuringia, Lower Saxony
Neighbours: Grand Est, Western Austria, Hesse, Bavaria, SCHWEIZ/SUISSE/SVIZZERA, Rhineland-Palatinate
Subregions: Stuttgart Government Region, Karlsruhe Government Region, Freiburg Government Region, Tübingen Government Region
Suggested citation: Michal Páleník: Europe and its regions in numbers - Baden-Württemberg – DE1, IZ Bratislava, retrieved from: https://www.iz.sk/PDE1, ISBN: 978-80-970204-9-1, DOI:10.5281/zenodo.10200164

 Share
Share Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter News
News