- About us»
- Net income calculator»
- Population aging»
-
-
- Unemployment structure in the Visegrad region
- Development in least developed regions
- Detailed statistics of least developed regions in Slovakia
- Statistics of the least developed regions in Slovakia
-
- Average wage
- Material need benefits
- Meal allowance
- Counties of Slovakia
- Inflation
- Living and Subsistence Minimum
- Unemployment of Czechia and Slovakia
- NACE Classification
-
- Life expectancy
- Gender differences
- Youth unemployment and NEET
- Minimum wage in EU
- Unemployment rates of different age groups
- Share of salaries on GDP
- Long term unemployment
- NEET
- Unemployment rate
- Employment rate
- Percentage of employees ususally working at nights
-
- Bratislava and surroundings
- Kopanice
- Danube river
- lower Vah river
- middle Vár river
- upper Nitra river
- lower Nitra river
- Mining cities
- Kysuce a Orava
- upper Vah river - Liptov
- Spiš cities
- upper Hron river
- Juhoslovenská kotlina
- Košice fold and Torysa river
- upper Zemplín
- lower Zemplín
- EU regions
- NUTS3 regions of Slovakia
- LAU1 dataset
-
-
- Projects and activities
- Inclusive growth»
- Good work
- Project SKRS
- Social system – reality and vision
- Library
-
- Education of unemployed
- Young unemployed not taking part in education
- Proposal to change the system of education funding
- News»
- Contact
Magdeburg – DEE03
EU regions: Germany > Saxony-Anhalt > Saxony-Anhalt > Magdeburg
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Gross domestic product | ||
| GDP per capita in PPS of EU average | 2023 | 99 |
Magdeburg slovensky: DEE03
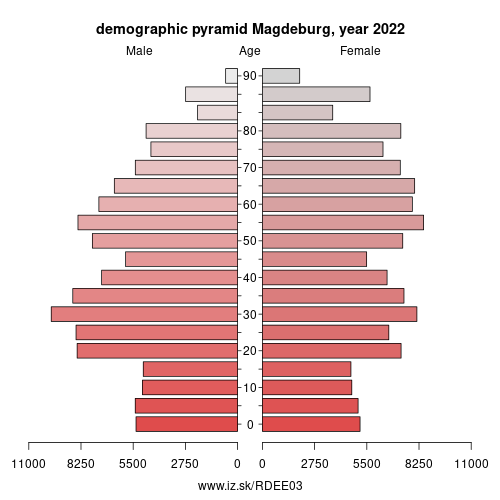
Demographics
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||
| number of inhabitants | 2025 | 244 329 |
| population density | 2024 | 1267.8 |
| old-age dependency ratio | 2025 | 38.6 |
From Wikipedia :
Magdeburg (German pronunciation: [ˈmakdəbʊɐ̯k] (listen); Low Saxon: Meideborg, [ˈmaˑɪdebɔɐ̯x]) is the capital city and the second largest city of the state of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is situated on the Elbe River.Otto I, the first Holy Roman Emperor and founder of the archbishopric of Magdeburg, was buried in the town's cathedral after his death. Magdeburg's version of German town law, known as Magdeburg rights, spread throughout Central and Eastern Europe. Until 1631, Magdeburg was one of the largest and most prosperous German cities, and a notable member of the Hanseatic League.
Magdeburg has been destroyed twice in its history. The Catholic League sacked Magdeburg in 1631, resulting in the death of 25,000 non-combatants, the largest loss of the Thirty Years' War. Allies bombed the city in 1945, destroying much of it.
Magdeburg is the site of two universities, the Otto-von-Guericke University and the Magdeburg-Stendal University of Applied Sciences.
Magdeburg is situated on autobahn route 2, and hence is at the connection point of the East (Berlin and beyond) with the West of Europe, as well as the North and South of Germany. As a modern manufacturing centre, the production of chemical products, steel, paper and textiles are of particular economic significance, along with mechanical engineering and plant engineering, ecotechnology and life-cycle management, health management and logistics.
Other: Saxony-Anhalt, Halle (Saale), Jerichower Land, Magdeburg, Anhalt-Bitterfeld, Harz District, Altmarkkreis Salzwedel, Salzlandkreis, Wittenberg, Saalekreis, Mansfeld-Südharz, Stendal District, Börde district, Dessau-Roßlau, Burgenlandkreis
Neighbours: Börde district, Jerichower Land, Salzlandkreis
Suggested citation: Michal Páleník: Europe and its regions in numbers - Magdeburg – DEE03, IZ Bratislava, retrieved from: https://www.iz.sk/PDEE03, ISBN: 978-80-970204-9-1, DOI:10.5281/zenodo.10200164

 Share
Share Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter News
News