- About us»
- Net income calculator»
- Population aging»
-
-
- Unemployment structure in the Visegrad region
- Development in least developed regions
- Detailed statistics of least developed regions in Slovakia
- Statistics of the least developed regions in Slovakia
-
- Average wage
- Material need benefits
- Meal allowance
- Counties of Slovakia
- Inflation
- Living and Subsistence Minimum
- Unemployment of Czechia and Slovakia
- NACE Classification
-
- Life expectancy
- Gender differences
- Youth unemployment and NEET
- Minimum wage in EU
- Unemployment rates of different age groups
- Share of salaries on GDP
- Long term unemployment
- NEET
- Unemployment rate
- Percentage of employees ususally working at nights
- Employment rate
-
- Bratislava and surroundings
- Kopanice
- Danube river
- lower Vah river
- middle Vár river
- upper Nitra river
- lower Nitra river
- Mining cities
- Kysuce a Orava
- upper Vah river - Liptov
- Spiš cities
- upper Hron river
- Juhoslovenská kotlina
- Košice fold and Torysa river
- upper Zemplín
- lower Zemplín
- EU regions
- NUTS3 regions of Slovakia
- LAU1 dataset
-
-
- Projects and activities
- Inclusive growth»
- Good work
- Project SKRS
- Social system – reality and vision
- Library
-
- Education of unemployed
- Young unemployed not taking part in education
- Proposal to change the system of education funding
- News»
- Contact
Kiel – DEF02
EU regions: Germany > Schleswig-Holstein > Schleswig-Holstein > Kiel
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Gross domestic product | ||
| GDP per capita in PPS of EU average | 2023 | 136 |
Kiel slovensky: DEF02
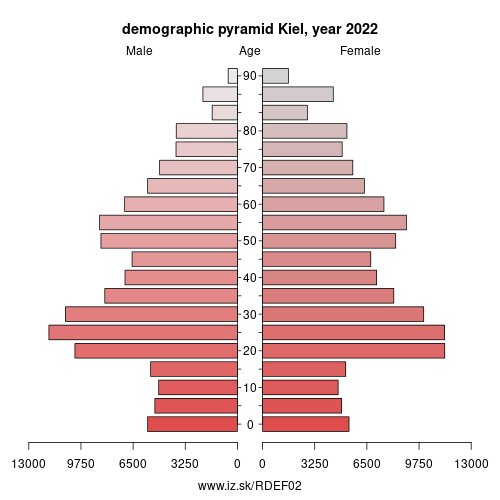
Demographics
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||
| number of inhabitants | 2025 | 252 668 |
| population density | 2023 | 2144.5 |
| old-age dependency ratio | 2025 | 28.5 |
From Wikipedia : Kiel (German: [kiːl] (listen)) is the capital and most populous city in the northern German state of Schleswig-Holstein, with a population of 249,023 (2016).
Kiel lies approximately 90 kilometres (56 mi) north of Hamburg. Due to its geographic location in the north of Germany, the southeast of the Jutland peninsula and the southwestern shore of the Baltic Sea, Kiel has become one of the major maritime centres of Germany. For instance, the city is known for a variety of international sailing events, including the annual Kiel Week, which is the biggest sailing event in the world. The Olympic sailing competitions of the 1936 and the 1972 Summer Olympics were held in the Bay of Kiel.
Kiel has also been one of the traditional homes of the German Navy's Baltic fleet, and continues to be a major high-tech shipbuilding centre. Located in Kiel is the GEOMAR – Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel at the University of Kiel. Kiel is an important sea transport hub, thanks to its location on the Kiel Fjord (Kieler Förde) and the busiest artificial waterway in the world, Kiel Canal (Nord-Ostsee-Kanal). A number of passenger ferries to Sweden, Norway, Lithuania and other countries operate from here. Moreover, today Kiel Harbour is an important port of call for cruise ships touring the Baltic Sea.
Kiel's recorded history began in the 13th century, but the city was originally a Danish village, in the 8th century.
Other: Schleswig-Holstein, District of Duchy of Lauenburg, Kreis Pinneberg, Segeberg District, Lübeck, Flensburg, Nordfriesland district, Rendsburg, Neumünster, Mittelangeln, Stormarn, Dithmarschen, Plön District, Ostholstein, Kiel, Steinburg
Neighbours: Plön District, Rendsburg
Suggested citation: Michal Páleník: Europe and its regions in numbers - Kiel – DEF02, IZ Bratislava, retrieved from: https://www.iz.sk/PDEF02, ISBN: 978-80-970204-9-1, DOI:10.5281/zenodo.10200164

 Share
Share Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter News
News