- About us»
- Net income calculator»
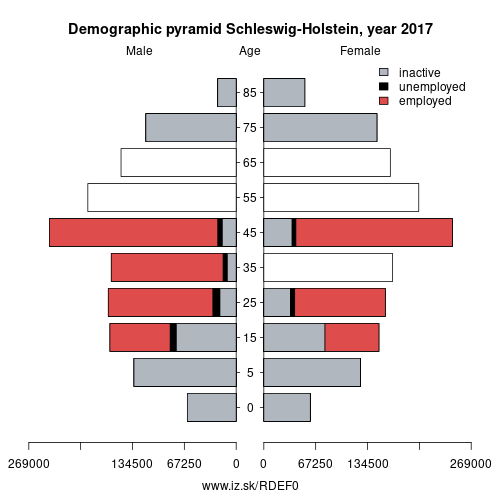
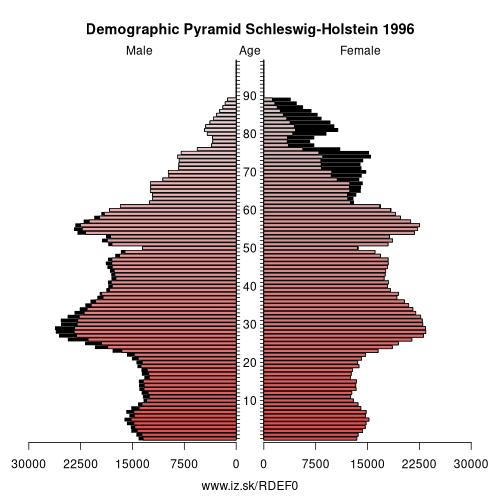
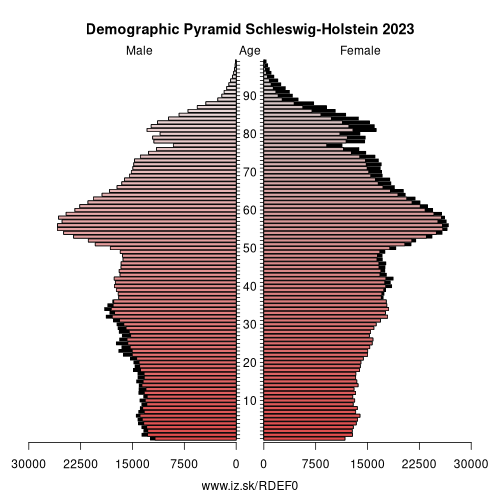
- Population aging»
-
-
- Unemployment structure in the Visegrad region
- Development in least developed regions
- Detailed statistics of least developed regions in Slovakia
- Statistics of the least developed regions in Slovakia
-
- Average wage
- Material need benefits
- Meal allowance
- Counties of Slovakia
- Inflation
- Living and Subsistence Minimum
- Unemployment of Czechia and Slovakia
- NACE Classification
-
- Life expectancy
- Gender differences
- Youth unemployment and NEET
- Minimum wage in EU
- Unemployment rates of different age groups
- Share of salaries on GDP
- Long term unemployment
- NEET
- Unemployment rate
- Employment rate
- Percentage of employees ususally working at nights
-
- Bratislava and surroundings
- Kopanice
- Danube river
- lower Vah river
- middle Vár river
- upper Nitra river
- lower Nitra river
- Mining cities
- Kysuce a Orava
- upper Vah river - Liptov
- Spiš cities
- upper Hron river
- Juhoslovenská kotlina
- Košice fold and Torysa river
- upper Zemplín
- lower Zemplín
- EU regions
- NUTS3 regions of Slovakia
- LAU1 dataset
-
-
- Projects and activities
- Inclusive growth»
- Good work
- Project SKRS
- Social system – reality and vision
- Library
-
- Education of unemployed
- Young unemployed not taking part in education
- Proposal to change the system of education funding
- News»
- Contact
Schleswig-Holstein – DEF0
EU regions: Germany > Schleswig-Holstein > Schleswig-Holstein
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Life long learning | ||
| life long learning participation | 2024 | 10.4 |
| Part time jobs and flexible employment | ||
| percentage of part time workers | 2024 | 33.33 |
| percentage of part time workers, men | 2024 | 15.49 |
| percentage of part time workers, women | 2024 | 53.44 |
| Gender differences | ||
| gender gap in employment rate | 2024 | 89.84 |
| gender gap in unemployment rate | 2024 | 91.43 |
| Graduates and young people | ||
| unemployment rate of youth with elementary education | 2019 | 9.3 |
| NEET | 2024 | 9.9 |
| Gross domestic product | ||
| GDP per capita in PPS of EU average | 2024 | 97 |
| Employment | ||
| employment rate | 2024 | 76.6 |
| Social exclusion | ||
| people at risk of poverty or social exclusion | 2019 | 20.8 |
Schleswig-Holstein slovensky: DEF0
Subregions: Flensburg, Kiel, Lübeck, Neumünster, Dithmarschen, District of Duchy of Lauenburg, Nordfriesland district, Ostholstein, Kreis Pinneberg, Plön District, Rendsburg, Mittelangeln, Segeberg District, Steinburg, Stormarn
Unemployment
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Unemployment | ||
| unemployment rate | 2024 | 3.5 |
| youth unemployment rate | 2019 | 6 |
| Long term unemployment | ||
| long term unemployment | 2024 | 0.9 |
| share of long term unemployed | 2024 | 27.2 |
Demographics
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||
| number of inhabitants | 2025 | 2 959 517 |
| population density | 2024 | 191.9 |
| old-age dependency ratio | 2025 | 38.3 |
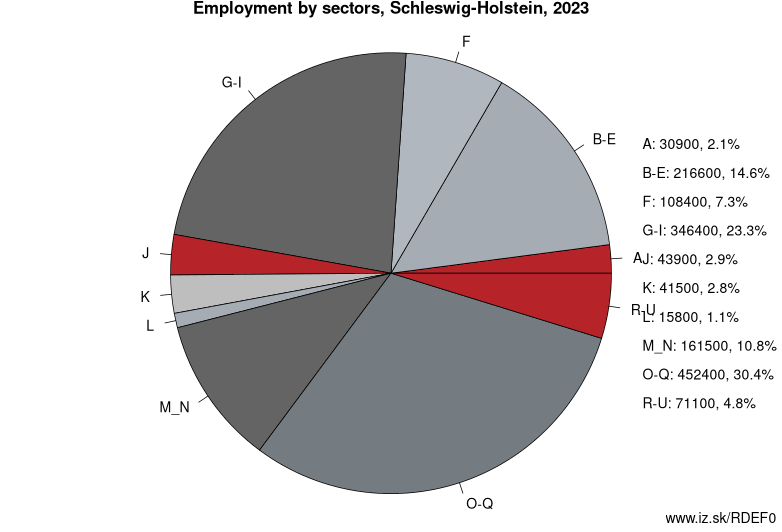
Employment by sectors, Schleswig-Holstein
| NACE r2 | % | NACE r2 | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 39.1 | 3% | B-E | 211.7 | 14% |
| F | 102.4 | 7% | G-I | 333 | 22% |
| J | 39 | 3% | K | 50.3 | 3% |
| L | 15.9 | 1% | M_N | 153.8 | 10% |
| O-Q | 482.4 | 32% | R-U | 62.3 | 4% |
| TOTAL | 1490 | 100% |
Data for the period year 2024. Source of the data is Eurostat, table [lfst_r_lfe2en2].
From Wikipedia :
Schleswig-Holstein (German: [ˈʃleːsvɪç ˈhɔlʃtaɪn]) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Schleswig. Its capital city is Kiel; other notable cities are Lübeck and Flensburg.Also known in more dated English as Sleswick-Holsatia, the region is called Slesvig-Holsten in Danish and pronounced [ˌsleːsvi ˈhɒlsteːˀn]. The Low German name is Sleswig-Holsteen, and the North Frisian name is Slaswik-Holstiinj. Historically, the name can also refer to a larger region, containing both present-day Schleswig-Holstein and the former South Jutland County (Northern Schleswig; now part of the Region of Southern Denmark) in Denmark.
History
The term „Holstein" derives from Old Saxon Holseta Land, (Holz and Holt mean wood in modern Standardised German and in literary English, respectively). Originally, it referred to the central of the three Saxon tribes north of the River Elbe: Tedmarsgoi (Dithmarschen), Holstein and Sturmarii (Stormarn). The area of the tribe of the Holsts was between the Stör River and Hamburg, and after Christianization, their main church was in Schenefeld. Saxon Holstein became a part of the Holy Roman Empire after Charlemagne's Saxon campaigns in the late eighth century. Since 811, the northern frontier of Holstein (and thus the Empire) was marked by the River Eider.
The term Schleswig comes from the city of Schleswig.
Other: Schleswig-Holstein, Schleswig-Holstein
Neighbours: Southern Denmark, Hamburg, Lüneburg Government Region, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
Subregions: Flensburg, Kiel, Lübeck, Neumünster, Dithmarschen, District of Duchy of Lauenburg, Nordfriesland district, Ostholstein, Kreis Pinneberg, Plön District, Rendsburg, Mittelangeln, Segeberg District, Steinburg, Stormarn
Suggested citation: Michal Páleník: Europe and its regions in numbers - Schleswig-Holstein – DEF0, IZ Bratislava, retrieved from: https://www.iz.sk/PDEF0, ISBN: 978-80-970204-9-1, DOI:10.5281/zenodo.10200164

 Share
Share Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter News
News