- About us»
- Net income calculator»
- Population aging»
-
-
- Unemployment structure in the Visegrad region
- Development in least developed regions
- Statistics of the least developed regions in Slovakia
- Detailed statistics of least developed regions in Slovakia
-
- Average wage
- Material need benefits
- Meal allowance
- Counties of Slovakia
- Inflation
- Living and Subsistence Minimum
- Unemployment of Czechia and Slovakia
- NACE Classification
-
- Life expectancy
- Gender differences
- Youth unemployment and NEET
- Minimum wage in EU
- Unemployment rates of different age groups
- Share of salaries on GDP
- Long term unemployment
- Percentage of employees ususally working at nights
- Employment rate
- Unemployment rate
- NEET
-
- Bratislava and surroundings
- Kopanice
- Danube river
- lower Vah river
- middle Vár river
- upper Nitra river
- lower Nitra river
- Mining cities
- Kysuce a Orava
- upper Vah river - Liptov
- Spiš cities
- upper Hron river
- Juhoslovenská kotlina
- Košice fold and Torysa river
- upper Zemplín
- lower Zemplín
- EU regions
- NUTS3 regions of Slovakia
- LAU1 dataset
-
-
- Projects and activities
- Inclusive growth»
- Good work
- Project SKRS
- Social system – reality and vision
-
- Education of unemployed
- Young unemployed not taking part in education
- Proposal to change the system of education funding
- Library
- News»
- Contact
Scotland – UKM
EU regions: United Kingdom > Scotland
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Life long learning | ||
| life long learning participation | 2019 | 14.7 |
| Part time jobs and flexible employment | ||
| percentage of part time workers | 2019 | 24.27 |
| percentage of part time workers, men | 2019 | 10.22 |
| percentage of part time workers, women | 2019 | 39.2 |
| Gender differences | ||
| gender gap in employment rate | 2019 | 91.48 |
| gender gap in unemployment rate | 2019 | 89.19 |
| Graduates and young people | ||
| unemployment rate of youth with elementary education | 2019 | 13.2 |
| NEET | 2019 | 9 |
| Employment | ||
| employment rate | 2019 | 74.1 |
Scotland slovensky: UKM
Subregions: North Eastern Scotland, Highlands and Islands, Eastern Scotland, West Central Scotland, Southern Scotland
Unemployment
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Unemployment | ||
| unemployment rate | 2019 | 3.6 |
| youth unemployment rate | 2019 | 7.4 |
| Long term unemployment | ||
| long term unemployment | 2019 | 1 |
| share of long term unemployed | 2019 | 29.9 |
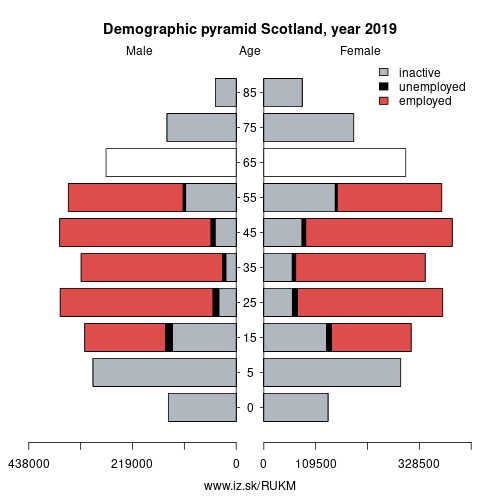
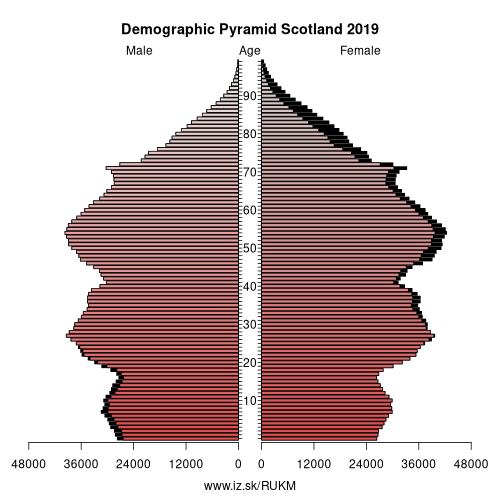
Demographics
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||
| number of inhabitants | 2019 | 5 454 238 |
| population density | 2018 | 69.9 |
| old-age dependency ratio | 2019 | 29.2 |
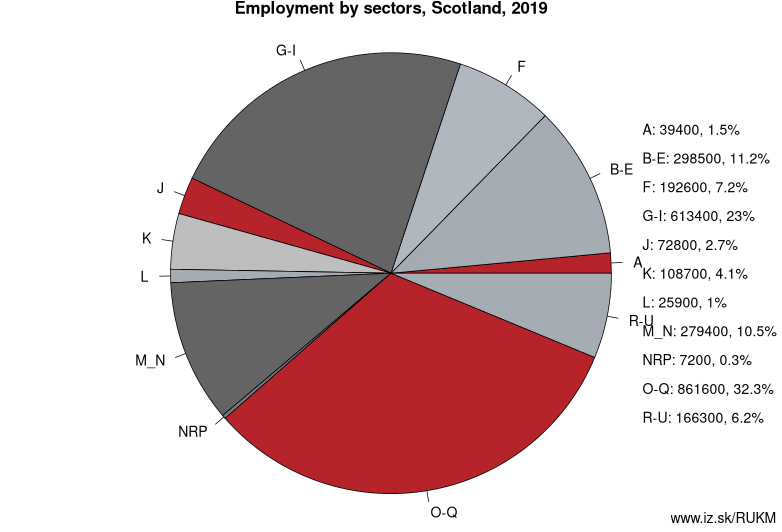
Employment by sectors, Scotland
| NACE r2 | % | NACE r2 | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 39.4 | 1% | B-E | 298.5 | 11% |
| F | 192.6 | 7% | G-I | 613.4 | 23% |
| J | 72.8 | 3% | K | 108.7 | 4% |
| L | 25.9 | 1% | M_N | 279.4 | 10% |
| NRP | 7.2 | 0% | O-Q | 861.6 | 32% |
| R-U | 166.3 | 6% | TOTAL | 2665.7 | 100% |
Data for the period year 2019. Source of the data is Eurostat, table [lfst_r_lfe2en2].
From Wikipedia :
Scotland (Scots: Scotland, Scottish Gaelic: Alba [ˈal̪ˠapə] (listen)) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It covers the northern third of the island of Great Britain, with a border with England to the southeast, and is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the northeast, the Irish Sea to the south, and more than 790 islands, including the Northern Isles and the Hebrides.
The Kingdom of Scotland emerged as an independent sovereign state in the Early Middle Ages and continued to exist until 1707. By inheritance in 1603, James VI, King of Scots, became King of England and King of Ireland, thus forming a personal union of the three kingdoms. Scotland subsequently entered into a political union with the Kingdom of England on 1 May 1707 to create the new Kingdom of Great Britain. The union also created a new Parliament of Great Britain, which succeeded both the Parliament of Scotland and the Parliament of England. In 1801, Great Britain itself entered into a political union with the Kingdom of Ireland to create the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (in 1922, the Irish Free State seceded from the United Kingdom, leading to the latter being renamed the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland).
Within Scotland, the monarchy of the United Kingdom has continued to use a variety of styles, titles and other royal symbols of statehood specific to the pre-union Kingdom of Scotland. The legal system within Scotland has also remained separate from those of England and Wales and Northern Ireland; Scotland constitutes a distinct jurisdiction in both public and private law. The continued existence of legal, educational, religious and other institutions distinct from those in the remainder of the UK have all contributed to the continuation of Scottish culture and national identity since the 1707 union with England.
In 1997, a Scottish Parliament was re-established, in the form of a devolved unicameral legislature comprising 129 members, having authority over many areas of domestic policy. The head of the Scottish Government is the First Minister of Scotland, who is supported by the Deputy First Minister of Scotland.
Other: United Kingdom, Northern Ireland, Wales, Scotland, Yorkshire and the Humber, Greater London, East Midlands, South West England, North East England, North West England, West Midlands, South East England, East of England
Neighbours: North West England, North East England
Subregions: North Eastern Scotland, Highlands and Islands, Eastern Scotland, West Central Scotland, Southern Scotland
Suggested citation: Michal Páleník: Europe and its regions in numbers - Scotland – UKM, IZ Bratislava, retrieved from: https://www.iz.sk/PUKM, ISBN: 978-80-970204-9-1, DOI:10.5281/zenodo.10200164

 Share
Share Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter News
News