- About us»
- Net income calculator»
- Population aging»
-
-
- Unemployment structure in the Visegrad region
- Development in least developed regions
- Detailed statistics of least developed regions in Slovakia
- Statistics of the least developed regions in Slovakia
-
- Average wage
- Material need benefits
- Meal allowance
- Counties of Slovakia
- Inflation
- Living and Subsistence Minimum
- Unemployment of Czechia and Slovakia
- NACE Classification
-
- Life expectancy
- Gender differences
- Youth unemployment and NEET
- Minimum wage in EU
- Unemployment rates of different age groups
- Share of salaries on GDP
- Percentage of employees ususally working at nights
- Unemployment rate
- Employment rate
- NEET
- Long term unemployment
-
- Bratislava and surroundings
- Kopanice
- Danube river
- lower Vah river
- middle Vár river
- upper Nitra river
- lower Nitra river
- Mining cities
- Kysuce a Orava
- upper Vah river - Liptov
- Spiš cities
- upper Hron river
- Juhoslovenská kotlina
- Košice fold and Torysa river
- upper Zemplín
- lower Zemplín
- EU regions
- NUTS3 regions of Slovakia
- LAU1 dataset
-
-
- Projects and activities
- Inclusive growth»
- Good work
- Project SKRS
- Social system – reality and vision
- Library
-
- Education of unemployed
- Young unemployed not taking part in education
- Proposal to change the system of education funding
- News»
- Contact
Cyprus – CY
Cyprus slovensky: CY
Unemployment
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Unemployment | ||
| unemployment rate | 2025q3 | 4.2 |
| youth unemployment rate | 2024 | 13 |
| unemployment rate of low educated people | 2025q3 | 5.1 |
| Long term unemployment | ||
| long term unemployment | 2025q3 | 0.8 |
| share of long term unemployed | 2025q3 | 18 |
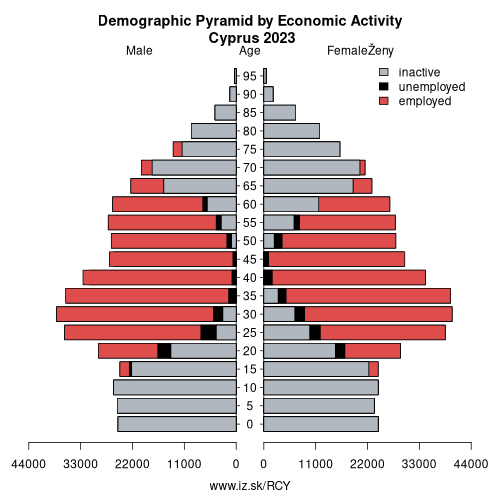
Composition of population according to age group, education and economic activity, Cyprus
| Age group | Low education | Middle education | High education |
|---|---|---|---|
| Y20-29 | P: 12.9 E: 7.3; U: 1.7; I: 3.9 | P: 51.1 E: 31.9; U: 4.1; I: 15.1 | P: 49.1 E: 40.9; U: 3.0; I: 5.2 |
| Y30-39 | P: 15.6 E: 12.8; U: 0.5; I: 2.3 | P: 40.3 E: 34.2; U: 1.9; I: 4.2 | P: 99.4 E: 87.5; U: 3.8; I: 8.1 |
| Y40-49 | P: 19.0 E: 14.2; U: 0.7; I: 4.1 | P: 44.3 E: 38.0; U: 1.7; I: 4.6 | P: 74.6 E: 66.0; U: 2.4; I: 6.2 |
| Y50-59 | P: 19.8 E: 13.6; U: 0.5; I: 5.7 | P: 54.4 E: 43.4; U: 1.7; I: 9.3 | P: 45.9 E: 40.0; U: 0.9; I: 5.0 |
| Y60-69 | P: 29.5 E: 10.7; U: 0.1; I: 18.7 | P: 43.6 E: 19.1; U: 0.7; I: 23.8 | P: 33.5 E: 17.0; U: 0.6; I: 15.9 |
Note: in thousands in 2024, according to labour force sample survey. P – total population, E – employed, U – unemployed, I – number of economically inactive
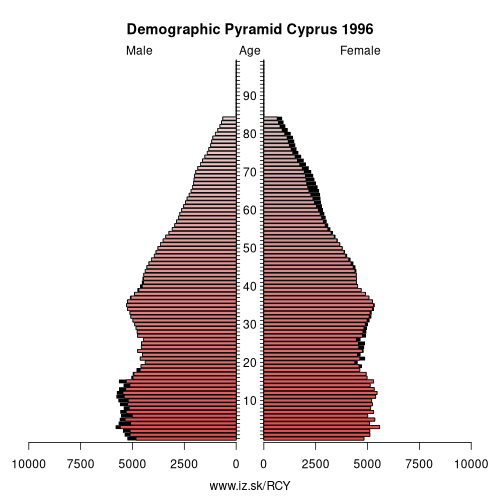
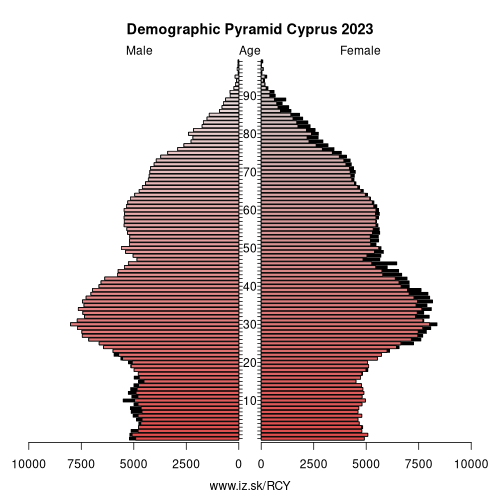
Demographics
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||
| number of inhabitants | 2025 | 982 966 |
| population density | 2024 | 105.8 |
| old-age dependency ratio | 2025 | 27.4 |
| Population ageing | ||
| unemployment rate – over 55 years | 2025q3 | 2.4 |
| aggregate replacement ratio | 2024 | 0.41 |
| aggregate replacement ratio – females | 2024 | 0.44 |
| life expectancy of a 50 year old | 2023 | 34.8 |
| healty life expectancy at 50 years | 2023 | 19.2 |
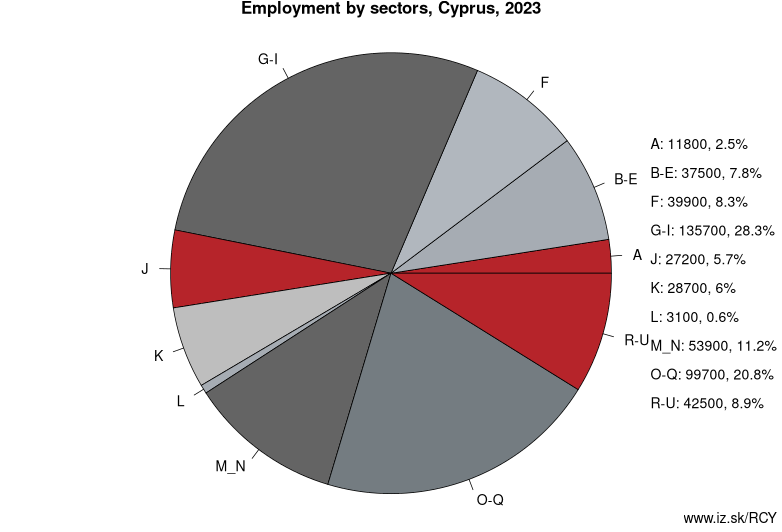
Employment by sectors, Cyprus
| NACE r2 | % | NACE r2 | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 10.7 | 2% | B-E | 35.8 | 7% |
| F | 43.9 | 9% | G-I | 141 | 29% |
| J | 26 | 5% | K | 25.9 | 5% |
| L | 3.4 | 1% | M_N | 53.6 | 11% |
| O-Q | 100.9 | 21% | R-U | 45.8 | 9% |
| TOTAL | 487 | 100% |
Data for the period year 2024. Source of the data is Eurostat, table [lfst_r_lfe2en2].
From Wikipedia :
Cyprus ( (listen); Greek: Κύπρος [ˈcipros]; Turkish: Kıbrıs [ˈkɯbɾɯs]), officially the Republic of Cyprus (Greek: Κυπριακή Δημοκρατία, lit. Cypriot Republic; Turkish: Kıbrıs Cumhuriyeti, lit. Republic of Cyprus), is an island country in the Eastern Mediterranean and the third largest and third most populous island in the Mediterranean, located south of Turkey, west of Syria and Lebanon, northwest of Israel and Palestine, north of Egypt, and southeast of Greece.The earliest known human activity on the island dates to around the 10th millennium BC. Archaeological remains from this period include the well-preserved Neolithic village of Khirokitia, and Cyprus is home to some of the oldest water wells in the world. Cyprus was settled by Mycenaean Greeks in two waves in the 2nd millennium BC. As a strategic location in the Middle East, it was subsequently occupied by several major powers, including the empires of the Assyrians, Egyptians and Persians, from whom the island was seized in 333 BC by Alexander the Great. Subsequent rule by Ptolemaic Egypt, the Classical and Eastern Roman Empire, Arab caliphates for a short period, the French Lusignan dynasty and the Venetians, was followed by over three centuries of Ottoman rule between 1571 and 1878 (de jure until 1914).
Cyprus was placed under the UK's administration based on the Cyprus Convention in 1878 and was formally annexed by the UK in 1914. While Turkish Cypriots made up 18 % of the population, the partition of Cyprus and creation of a Turkish state in the north became a policy of Turkish Cypriot leaders and Turkey in the 1950s. Turkish leaders for a period advocated the annexation of Cyprus to Turkey as Cyprus was considered an „extension of Anatolia" by them; while, since the 19th century, the majority Greek Cypriot population and its Orthodox church had been pursuing union with Greece, which became a Greek national policy in the 1950s. Following nationalist violence in the 1950s, Cyprus was granted independence in 1960. The crisis of 1963–64 brought further intercommunal violence between Greek Cypriots and Turkish Cypriots, which displaced more than 25,000 Turkish Cypriots into enclaves and brought the end of Turkish Cypriot representation in the republic. On 15 July 1974, a coup d'état was staged by Greek Cypriot nationalists and elements of the Greek military junta in an attempt at enosis, the incorporation of Cyprus into Greece. This action precipitated the Turkish invasion of Cyprus on 20 July, which led to the capture of the present-day territory of Northern Cyprus in the following month, after a ceasefire collapsed, and the displacement of over 150,000 Greek Cypriots and 50,000 Turkish Cypriots.
Other: Switzerland, Cyprus, Czech Republic
Suggested citation: Michal Páleník: Europe and its regions in numbers - Cyprus – CY, IZ Bratislava, retrieved from: https://www.iz.sk/PCY, ISBN: 978-80-970204-9-1, DOI:10.5281/zenodo.10200164

 Share
Share Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter News
News