- About us»
- Net income calculator»
- Population aging»
-
-
- Unemployment structure in the Visegrad region
- Development in least developed regions
- Detailed statistics of least developed regions in Slovakia
- Statistics of the least developed regions in Slovakia
-
- Average wage
- Material need benefits
- Meal allowance
- Counties of Slovakia
- Inflation
- Living and Subsistence Minimum
- Unemployment of Czechia and Slovakia
- NACE Classification
-
- Life expectancy
- Gender differences
- Youth unemployment and NEET
- Minimum wage in EU
- Unemployment rates of different age groups
- Share of salaries on GDP
- Long term unemployment
- Percentage of employees ususally working at nights
- NEET
- Unemployment rate
- Employment rate
-
- Bratislava and surroundings
- Kopanice
- Danube river
- lower Vah river
- middle Vár river
- upper Nitra river
- lower Nitra river
- Mining cities
- Kysuce a Orava
- upper Vah river - Liptov
- Spiš cities
- upper Hron river
- Juhoslovenská kotlina
- Košice fold and Torysa river
- upper Zemplín
- lower Zemplín
- EU regions
- NUTS3 regions of Slovakia
- LAU1 dataset
-
-
- Projects and activities
- Inclusive growth»
- Good work
- Project SKRS
- Social system – reality and vision
- Library
-
- Education of unemployed
- Young unemployed not taking part in education
- Proposal to change the system of education funding
- News»
- Contact
Wuppertal – DEA1A
EU regions: Germany > North Rhine-Westphalia > Düsseldorf Government Region > Wuppertal
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Gross domestic product | ||
| GDP per capita in PPS of EU average | 2023 | 94 |
Wuppertal slovensky: DEA1A
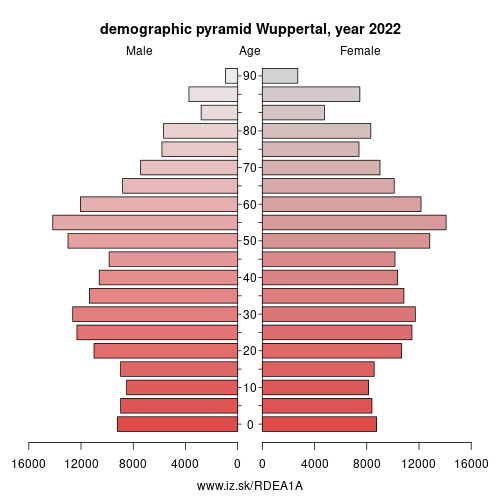
Demographics
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||
| number of inhabitants | 2025 | 358 193 |
| population density | 2024 | 2133.3 |
| old-age dependency ratio | 2025 | 32.8 |
From Wikipedia : Wuppertal (German pronunciation: [ˈvʊpɐtaːl] (listen)) is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, in and around the Wupper valley, east of Düsseldorf and south of the Ruhr. With a population of approximately 350,000, it is the largest city in the Bergisches Land. Wuppertal is known for its steep slopes, its woods and parks, and its suspension railway, the Wuppertal Schwebebahn. It is the greenest city of Germany, with two-thirds green space of the total municipal area. From any part of the city, it is only a ten-minute walk to one of the public parks or woodland paths.
In the 18th and 19th centuries, the Wupper valley was one of the largest industrial regions of continental Europe. The increasing demand for coal from the textile mills and blacksmith shops encouraged the expansion of the nearby Ruhrgebiet. Wuppertal still is a major industrial centre, being home to industries such as textiles, metallurgy, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, electronics, automobiles, rubber, vehicles and printing equipment.
Aspirin originates from Wuppertal, patented in 1897 by Bayer, as is the Vorwerk-Kobold vacuum cleaner.
The Wuppertal Institute for Climate, Environment and Energy and the European Institute for International Economic Relations are located in the city.
History
Wuppertal in its present borders was formed in 1929 by merging the industrial cities of Barmen and Elberfeld with the communities Vohwinkel, Ronsdorf, Cronenberg, Langerfeld and Beyenburg. The initial name Barmen-Elberfeld was changed in a 1930 referendum to Wuppertal (“Wupper Valley”).
Other: Düsseldorf Government Region, Mönchengladbach, Remscheid, Rhein-Kreis Neuss, Duisburg, Kleve, Mettmann, Düsseldorf, Wuppertal, Oberhausen, Mülheim an der Ruhr, Krefeld, Viersen, Solingen, Essen, Wesel
Neighbours: Oberbergischer Kreis, Ennepe-Ruhr-Kreis, Mettmann, Solingen, Remscheid
Suggested citation: Michal Páleník: Europe and its regions in numbers - Wuppertal – DEA1A, IZ Bratislava, retrieved from: https://www.iz.sk/PDEA1A, ISBN: 978-80-970204-9-1, DOI:10.5281/zenodo.10200164

 Share
Share Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter News
News