- About us»
- Net income calculator»
- Population aging»
-
-
- Unemployment structure in the Visegrad region
- Development in least developed regions
- Detailed statistics of least developed regions in Slovakia
- Statistics of the least developed regions in Slovakia
-
- Average wage
- Material need benefits
- Meal allowance
- Counties of Slovakia
- Inflation
- Living and Subsistence Minimum
- Unemployment of Czechia and Slovakia
- NACE Classification
-
- Life expectancy
- Gender differences
- Youth unemployment and NEET
- Minimum wage in EU
- Unemployment rates of different age groups
- Share of salaries on GDP
- Long term unemployment
- Percentage of employees ususally working at nights
- NEET
- Employment rate
- Unemployment rate
-
- Bratislava and surroundings
- Kopanice
- Danube river
- lower Vah river
- middle Vár river
- upper Nitra river
- lower Nitra river
- Mining cities
- Kysuce a Orava
- upper Vah river - Liptov
- Spiš cities
- upper Hron river
- Juhoslovenská kotlina
- Košice fold and Torysa river
- upper Zemplín
- lower Zemplín
- EU regions
- NUTS3 regions of Slovakia
- LAU1 dataset
-
-
- Projects and activities
- Inclusive growth»
- Good work
- Project SKRS
- Social system – reality and vision
- Library
-
- Education of unemployed
- Young unemployed not taking part in education
- Proposal to change the system of education funding
- News»
- Contact
Essen – DEA13
EU regions: Germany > North Rhine-Westphalia > Düsseldorf Government Region > Essen
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Gross domestic product | ||
| GDP per capita in PPS of EU average | 2023 | 127 |
Essen slovensky: DEA13
Demographics
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||
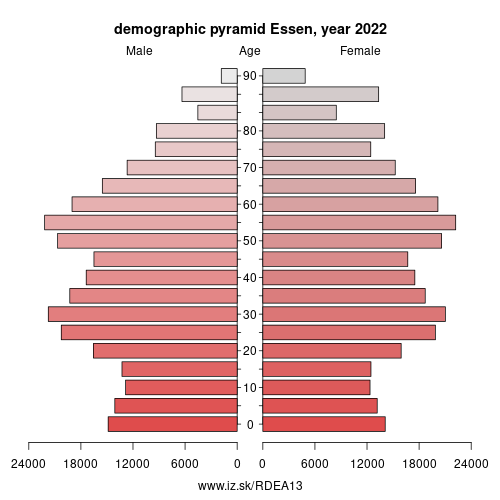
| number of inhabitants | 2025 | 574 682 |
| population density | 2024 | 2774.8 |
| old-age dependency ratio | 2025 | 34.4 |
From Wikipedia : Essen (German pronunciation: [ˈɛsn̩] (listen); Latin: Assindia) is the central and second largest city of the Ruhr, the largest urban area in Germany. Its population of 583,393 makes it the ninth largest city of Germany, as well as the fourth largest city of the federal state of North Rhine-Westphalia. On the Ruhr and Emscher rivers, Essen geographically is part of the Rhineland and the larger Rhine-Ruhr Metropolitan Region. The Ruhrdeutsch regiolect spoken in the region has strong influences of both Low German (Westphalian) and Low Franconian (East Bergish).
Essen is seat to several of the region's authorities, as well as to eight of the 100 largest publicly held German corporations regarding turnover, including three DAX corporations, placing Essen first among all German cities in the number of DAX corporate headquarters, together with Munich. Essen is often considered the energy capital of Germany with E.ON and RWE, Germany's largest energy providers, both headquartered in the city. Essen is also known for its impact on the arts through the respected Folkwang University of the Arts, its Zollverein School of Management and Design, and the Red Dot industrial product design award. In early 2003, the universities of Essen and the nearby city of Duisburg (both established in 1972) were merged into the University of Duisburg-Essen with campuses in both cities and a university hospital in Essen. In 1958, Essen was chosen to serve as the seat to a Roman Catholic diocese (often referred to as Ruhrbistum or diocese of the Ruhr).
Founded around 845, Essen remained a small town within the sphere of influence of an important ecclesiastical principality (Essen Abbey) until the onset of industrialization.
Other: Düsseldorf Government Region, Mönchengladbach, Remscheid, Rhein-Kreis Neuss, Duisburg, Kleve, Mettmann, Düsseldorf, Wuppertal, Oberhausen, Mülheim an der Ruhr, Krefeld, Viersen, Solingen, Essen, Wesel
Neighbours: Bottrop, Mülheim an der Ruhr, Ennepe-Ruhr-Kreis, Recklinghausen, Gelsenkirchen, Mettmann, Bochum, Oberhausen
Suggested citation: Michal Páleník: Europe and its regions in numbers - Essen – DEA13, IZ Bratislava, retrieved from: https://www.iz.sk/PDEA13, ISBN: 978-80-970204-9-1, DOI:10.5281/zenodo.10200164

 Share
Share Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter News
News