- About us»
- Net income calculator»
- Population aging»
-
-
- Unemployment structure in the Visegrad region
- Development in least developed regions
- Statistics of the least developed regions in Slovakia
- Detailed statistics of least developed regions in Slovakia
-
- Average wage
- Material need benefits
- Meal allowance
- Counties of Slovakia
- Inflation
- Living and Subsistence Minimum
- Unemployment of Czechia and Slovakia
- NACE Classification
-
- Life expectancy
- Gender differences
- Youth unemployment and NEET
- Minimum wage in EU
- Unemployment rates of different age groups
- Share of salaries on GDP
- Unemployment rate
- Percentage of employees ususally working at nights
- Employment rate
- NEET
- Long term unemployment
-
- Bratislava and surroundings
- Kopanice
- Danube river
- lower Vah river
- middle Vár river
- upper Nitra river
- lower Nitra river
- Mining cities
- Kysuce a Orava
- upper Vah river - Liptov
- Spiš cities
- upper Hron river
- Juhoslovenská kotlina
- Košice fold and Torysa river
- upper Zemplín
- lower Zemplín
- EU regions
- NUTS3 regions of Slovakia
- LAU1 dataset
-
-
- Projects and activities
- Inclusive growth»
- Good work
- Project SKRS
- Social system – reality and vision
- Library
-
- Education of unemployed
- Young unemployed not taking part in education
- Proposal to change the system of education funding
- News»
- Contact
Mainz – DEB35
EU regions: Germany > Rhineland-Palatinate > Rheinhessen-Pfalz > Mainz
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Gross domestic product | ||
| GDP per capita in PPS of EU average | 2023 | 205 |
Mainz slovensky: DEB35
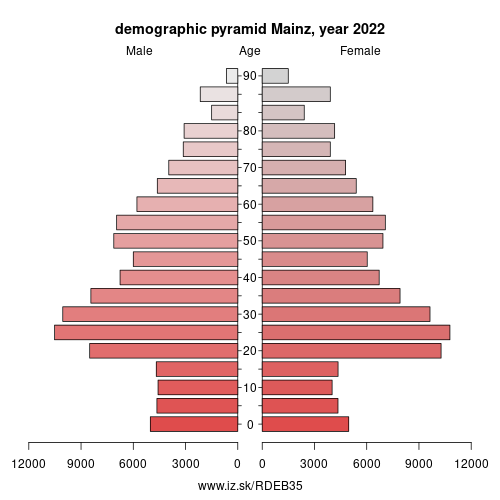
Demographics
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||
| number of inhabitants | 2025 | 224 684 |
| population density | 2023 | 2344.1 |
| old-age dependency ratio | 2025 | 25.9 |
From Wikipedia : Mainz ( MYNTS, German: [maɪnts] (listen) is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. The city is located on the Rhine river at its confluence with the Main river, opposite Wiesbaden on the border with Hesse. Mainz is an independent city with a population of 217,118 (2018) and forms part of the Frankfurt Rhine-Main Metropolitan Region.
Mainz was founded as Mogontiacum by the Romans in the 1st Century BC during Classical antiquity, serving as a military fortress on the northernmost frontier of the Roman Empire and as the provincial capital of Germania Superior. Mainz became an important city in the 8th Century AD as part of the Holy Roman Empire, becoming the capital of the Electorate of Mainz and seat of the Archbishop-Elector of Mainz, the Primate of Germany. Mainz is famous as the home of Johannes Gutenberg, the inventor of the movable-type printing press, who in the early 1450s manufactured his first books in the city, including the Gutenberg Bible. Historically, before the 20th century, the city was known in English as Mentz and in French as Mayence. Mainz was heavily damaged during World War II, with more than 30 air raids destroying about 80 percent of the city's center, including most of the historic buildings. Today, Mainz is a transport hub and a center of wine production.
Geography
Topography
Mainz is located on the 50th latitude, on the left bank of the river Rhine, opposite the confluence of the Main with the Rhine. The population in the early 2012 was 200,957, an additional 18,619 people maintain a primary residence elsewhere but have a second home in Mainz.
Other: Rheinhessen-Pfalz, Neustadt an der Weinstraße, Pirmasens, Worms, Zweibrücken, Donnersbergkreis, Germersheim, Kaiserslautern, Bad Dürkheim, Südliche Weinstraße, Kaiserslautern, Landau in der Pfalz, Ludwigshafen, Speyer, Südwestpfalz, Kusel, Frankenthal, Rhein-Pfalz, Alzey-Worms district, Mainz, Mainz-Bingen district
Neighbours: Groß-Gerau, Wiesbaden, Mainz-Bingen district
Suggested citation: Michal Páleník: Europe and its regions in numbers - Mainz – DEB35, IZ Bratislava, retrieved from: https://www.iz.sk/PDEB35, ISBN: 978-80-970204-9-1, DOI:10.5281/zenodo.10200164

 Share
Share Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter News
News