- About us»
- Net income calculator»
- Population aging»
-
-
- Unemployment structure in the Visegrad region
- Development in least developed regions
- Detailed statistics of least developed regions in Slovakia
- Statistics of the least developed regions in Slovakia
-
- Average wage
- Material need benefits
- Meal allowance
- Counties of Slovakia
- Inflation
- Living and Subsistence Minimum
- Unemployment of Czechia and Slovakia
- NACE Classification
-
- Life expectancy
- Gender differences
- Youth unemployment and NEET
- Minimum wage in EU
- Unemployment rates of different age groups
- Share of salaries on GDP
- Long term unemployment
- Percentage of employees ususally working at nights
- NEET
- Unemployment rate
- Employment rate
-
- Bratislava and surroundings
- Kopanice
- Danube river
- lower Vah river
- middle Vár river
- upper Nitra river
- lower Nitra river
- Mining cities
- Kysuce a Orava
- upper Vah river - Liptov
- Spiš cities
- upper Hron river
- Juhoslovenská kotlina
- Košice fold and Torysa river
- upper Zemplín
- lower Zemplín
- EU regions
- NUTS3 regions of Slovakia
- LAU1 dataset
-
-
- Projects and activities
- Inclusive growth»
- Good work
- Project SKRS
- Social system – reality and vision
- Library
-
- Education of unemployed
- Young unemployed not taking part in education
- Proposal to change the system of education funding
- News»
- Contact
Serbia – RS
Serbia slovensky: RS
Subregions: Serbia-North, Serbia-South
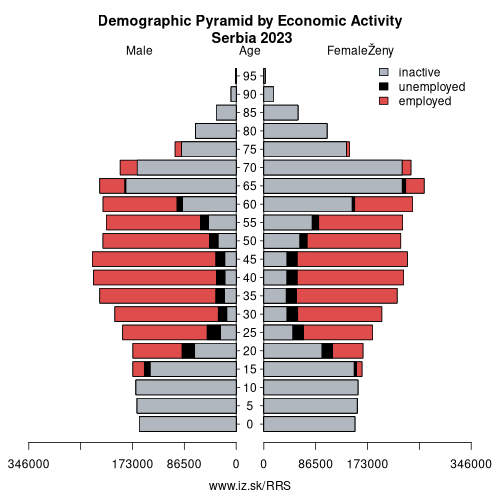
Unemployment
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Unemployment | ||
| unemployment rate | 2025q3 | 8.5 |
| youth unemployment rate | 2024 | 23 |
| unemployment rate of low educated people | 2025q3 | 11.9 |
| Long term unemployment | ||
| long term unemployment | 2025q3 | 3.4 |
| share of long term unemployed | 2024 | 40 |
Composition of population according to age group, education and economic activity, Serbia
| Age group | Low education | Middle education | High education |
|---|---|---|---|
| Y20-29 | P: 50.7 E: 22.5; U: 9.5; I: 18.7 | P: 494.5 E: 265.0; U: 44.5; I: 185.0 | P: 151.5 E: 111.0; U: 18.6; I: 21.9 |
| Y30-39 | P: 82.2 E: 45.6; U: 10.2; I: 26.4 | P: 414.4 E: 336.5; U: 34.0; I: 43.9 | P: 324.2 E: 284.5; U: 22.1; I: 17.6 |
| Y40-49 | P: 138.1 E: 83.5; U: 10.8; I: 43.8 | P: 533.1 E: 443.8; U: 31.1; I: 58.2 | P: 275.5 E: 251.8; U: 11.4; I: 12.3 |
| Y50-59 | P: 165.0 E: 90.1; U: 10.4; I: 64.5 | P: 547.3 E: 402.6; U: 31.6; I: 113.1 | P: 184.1 E: 159.2; U: 7.6; I: 17.3 |
| Y60-69 | P: 247.0 E: 67.4; U: 3.9; I: 175.7 | P: 504.4 E: 158.9; U: 10.2; I: 335.3 | P: 171.5 E: 77.7; U: 2.0; I: 91.8 |
Note: in thousands in 2024, according to labour force sample survey. P – total population, E – employed, U – unemployed, I – number of economically inactive
Demographics
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||
| number of inhabitants | 2025 | 6 567 783 |
| population density | 2019 | 90.5 |
| old-age dependency ratio | 2025 | 36.2 |
| Population ageing | ||
| unemployment rate – over 55 years | 2025q3 | 5.6 |
| aggregate replacement ratio | 2024 | 0.48 |
| aggregate replacement ratio – females | 2024 | 0.48 |
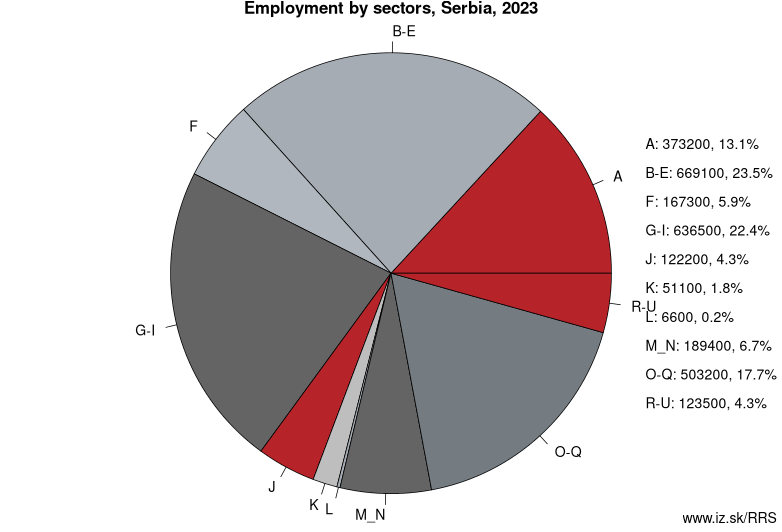
Employment by sectors, Serbia
| NACE r2 | % | NACE r2 | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 371.9 | 13% | B-E | 667 | 23% |
| F | 173.3 | 6% | G-I | 652.9 | 23% |
| J | 125.9 | 4% | K | 52.3 | 2% |
| L | 8.8 | 0% | M_N | 193.8 | 7% |
| O-Q | 526.5 | 18% | R-U | 125.1 | 4% |
| TOTAL | 2897.5 | 100% |
Data for the period year 2024. Source of the data is Eurostat, table [lfst_r_lfe2en2].
From Wikipedia : Serbia (Serbian: Србија, romanized: Srbija, pronounced [sř̩bija]), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: Република Србија, romanized: Republika Srbija, pronounced [repǔblika sř̩bija]), is a country situated at the crossroads of Central and Southeast Europe in the southern Pannonian Plain and the central Balkans. It borders Hungary to the north, Romania to the northeast, Bulgaria to the southeast, North Macedonia to the south, Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina to the west, and Montenegro to the southwest. The country claims a border with Albania through the disputed territory of Kosovo. Serbia's population numbers approximately seven million, most of whom are Orthodox Christians. Its capital, Belgrade, ranks among the longest inhabited and largest citiеs in southeastern Europe.
Inhabited since the Paleolithic Age, the territory of modern-day Serbia faced Slavic migrations to the Southeastern Europe in the 6th century, establishing several regional states in the early Middle Ages at times recognised as tributaries to the Byzantine, Frankish and Hungarian kingdoms. The Serbian Kingdom obtained recognition by the Holy See and Constantinople in 1217, reaching its territorial apex in 1346 as the relatively short-lived Serbian Empire. By the mid-16th century, the entirety of modern-day Serbia was annexed by the Ottomans; their rule was at times interrupted by the Habsburg Empire, which began expanding towards Central Serbia from the end of the 17th century while maintaining a foothold in Vojvodina. In the early 19th century, the Serbian Revolution established the nation-state as the region's first constitutional monarchy, which subsequently expanded its territory. Following disastrous casualties in World War I, and the subsequent unification of the former Habsburg crownland of Vojvodina (and other territories) with Serbia, the country co-founded Yugoslavia with other South Slavic peoples, which would exist in various political formations until the Yugoslav Wars of the 1990s. During the breakup of Yugoslavia, Serbia formed a union with Montenegro, which was peacefully dissolved in 2006.
Neighbours: Montenegro, Romania, Croatia, North Macedonia, Bulgaria, Hungary
Subregions: Serbia-North, Serbia-South
Suggested citation: Michal Páleník: Europe and its regions in numbers - Serbia – RS, IZ Bratislava, retrieved from: https://www.iz.sk/PRS, ISBN: 978-80-970204-9-1, DOI:10.5281/zenodo.10200164

 Share
Share Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter News
News