- About us»
- Net income calculator»
- Population aging»
-
-
- Unemployment structure in the Visegrad region
- Development in least developed regions
- Detailed statistics of least developed regions in Slovakia
- Statistics of the least developed regions in Slovakia
-
- Average wage
- Material need benefits
- Meal allowance
- Counties of Slovakia
- Inflation
- Living and Subsistence Minimum
- Unemployment of Czechia and Slovakia
- NACE Classification
-
- Life expectancy
- Gender differences
- Youth unemployment and NEET
- Minimum wage in EU
- Unemployment rates of different age groups
- Share of salaries on GDP
- Long term unemployment
- NEET
- Unemployment rate
- Percentage of employees ususally working at nights
- Employment rate
-
- Bratislava and surroundings
- Kopanice
- Danube river
- lower Vah river
- middle Vár river
- upper Nitra river
- lower Nitra river
- Mining cities
- Kysuce a Orava
- upper Vah river - Liptov
- Spiš cities
- upper Hron river
- Juhoslovenská kotlina
- Košice fold and Torysa river
- upper Zemplín
- lower Zemplín
- EU regions
- NUTS3 regions of Slovakia
- LAU1 dataset
-
-
- Projects and activities
- Inclusive growth»
- Good work
- Project SKRS
- Social system – reality and vision
- Library
-
- Education of unemployed
- Young unemployed not taking part in education
- Proposal to change the system of education funding
- News»
- Contact
Malta – MT00
EU regions: Malta > Malta > Malta
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Life long learning | ||
| life long learning participation | 2024 | 18.6 |
| Part time jobs and flexible employment | ||
| percentage of part time workers | 2024 | 9.67 |
| percentage of part time workers, men | 2024 | 4.84 |
| percentage of part time workers, women | 2024 | 16.82 |
| Gender differences | ||
| gender gap in employment rate | 2024 | 84.49 |
| gender gap in unemployment rate | 2024 | 90.91 |
| Graduates and young people | ||
| unemployment rate of youth with elementary education | 2024 | 13 |
| NEET | 2024 | 7.6 |
| Gross domestic product | ||
| GDP per capita in PPS of EU average | 2024 | 110 |
| Employment | ||
| employment rate | 2024 | 79.2 |
Malta slovensky: MT00
Subregions: Malta, Gozo and Comino/Għawdex u Kemmuna
Unemployment
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Unemployment | ||
| unemployment rate | 2024 | 3.2 |
| youth unemployment rate | 2024 | 9.2 |
| Long term unemployment | ||
| long term unemployment | 2024 | 0.7 |
| share of long term unemployed | 2024 | 21.4 |
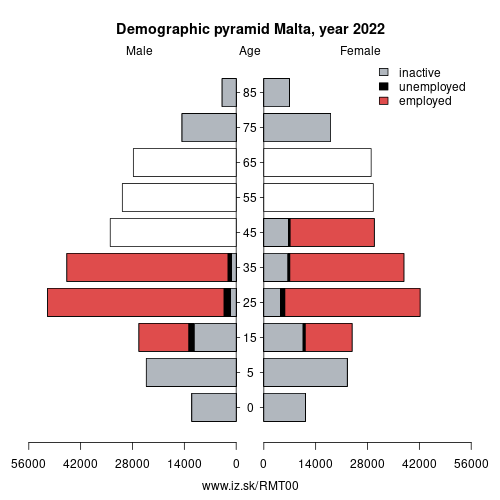
Demographics
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||
| number of inhabitants | 2025 | 574 250 |
| population density | 2024 | 1817.4 |
| old-age dependency ratio | 2025 | 26.6 |
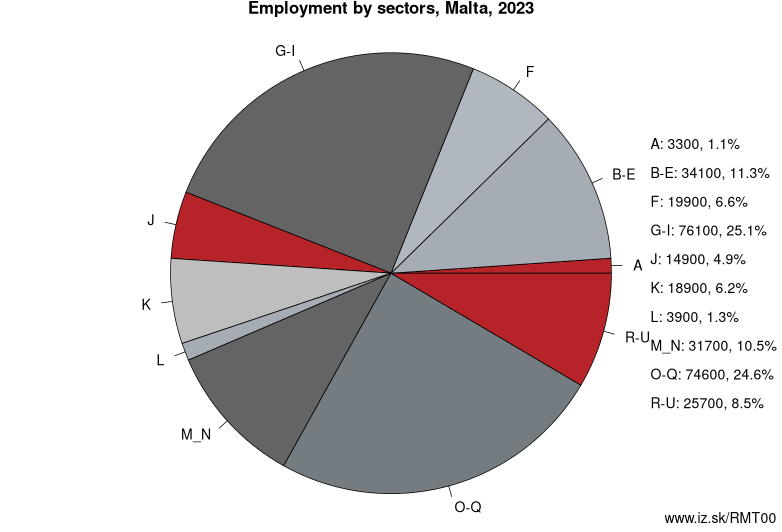
Employment by sectors, Malta
| NACE r2 | % | NACE r2 | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2.9 | 1% | B-E | 34.5 | 11% |
| F | 22.2 | 7% | G-I | 79.1 | 25% |
| J | 15.7 | 5% | K | 19.4 | 6% |
| L | 2.7 | 1% | M_N | 32 | 10% |
| O-Q | 81.1 | 26% | R-U | 28.1 | 9% |
| TOTAL | 317.7 | 100% |
Data for the period year 2024. Source of the data is Eurostat, table [lfst_r_lfe2en2].
From Wikipedia :
Malta (, (listen); in Maltese: [ˈmɐltɐ]; Italian: [ˈmalta]), officially known as the Republic of Malta (Maltese: Repubblika ta' Malta) and formerly Melita, is a Southern European island country consisting of an archipelago in the Mediterranean Sea. It lies 80 km (50 mi) south of Italy, 284 km (176 mi) east of Tunisia, and 333 km (207 mi) north of Libya. With a population of about 515,000 over an area of 316 km2 (122 sq mi), Malta is the world's tenth smallest country in area and fourth most densely populated sovereign country. Its capital is Valletta, which is the smallest national capital in the European Union by area at 0.61 km2 (0.24 sq mi). The official and national language is Maltese, which is descended from Sicilian Arabic that developed during the Emirate of Sicily, while English serves as the second official language. Italian and Sicilian also previously served as official and cultural languages on the island for centuries, with Italian being an official language in Malta until 1934 and a majority of the current Maltese population being at least conversational in the Italian language.Malta has been inhabited since approximately 5900 BC. Its location in the centre of the Mediterranean has historically given it great strategic importance as a naval base, with a succession of powers having contested and ruled the islands, including the Phoenicians and Carthaginians, Romans, Greeks, Arabs, Normans, Aragonese, Knights of St. John, French, and British. Most of these foreign influences have left some sort of mark on the country's ancient culture.
Malta became a British colony in 1813, serving as a way station for ships and the headquarters for the British Mediterranean Fleet.
Subregions: Malta, Gozo and Comino/Għawdex u Kemmuna
Suggested citation: Michal Páleník: Europe and its regions in numbers - Malta – MT00, IZ Bratislava, retrieved from: https://www.iz.sk/PMT00, ISBN: 978-80-970204-9-1, DOI:10.5281/zenodo.10200164

 Share
Share Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter News
News