- About us»
- Net income calculator»
- Population aging»
-
-
- Unemployment structure in the Visegrad region
- Development in least developed regions
- Detailed statistics of least developed regions in Slovakia
- Statistics of the least developed regions in Slovakia
-
- Average wage
- Material need benefits
- Meal allowance
- Counties of Slovakia
- Inflation
- Living and Subsistence Minimum
- Unemployment of Czechia and Slovakia
- NACE Classification
-
- Life expectancy
- Gender differences
- Youth unemployment and NEET
- Minimum wage in EU
- Unemployment rates of different age groups
- Share of salaries on GDP
- Percentage of employees ususally working at nights
- Unemployment rate
- Employment rate
- NEET
- Long term unemployment
-
- Bratislava and surroundings
- Kopanice
- Danube river
- lower Vah river
- middle Vár river
- upper Nitra river
- lower Nitra river
- Mining cities
- Kysuce a Orava
- upper Vah river - Liptov
- Spiš cities
- upper Hron river
- Juhoslovenská kotlina
- Košice fold and Torysa river
- upper Zemplín
- lower Zemplín
- EU regions
- NUTS3 regions of Slovakia
- LAU1 dataset
-
-
- Projects and activities
- Inclusive growth»
- Good work
- Project SKRS
- Social system – reality and vision
- Library
-
- Education of unemployed
- Young unemployed not taking part in education
- Proposal to change the system of education funding
- News»
- Contact
Weimar – DEG05
EU regions: Germany > Thuringia > Thuringia > Weimar
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Gross domestic product | ||
| GDP per capita in PPS of EU average | 2023 | 86 |
Weimar slovensky: DEG05
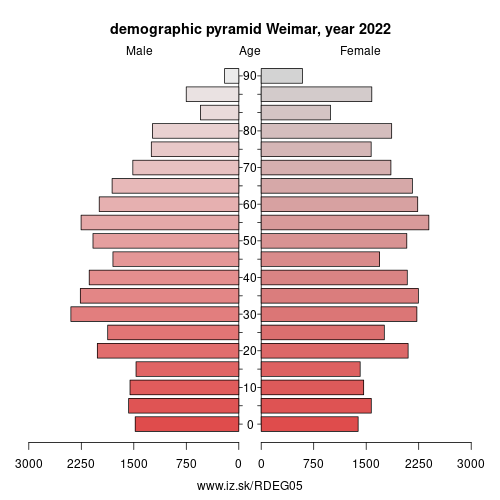
Demographics
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||
| number of inhabitants | 2025 | 65 954 |
| population density | 2023 | 780 |
| old-age dependency ratio | 2025 | 39.7 |
From Wikipedia : Weimar (German pronunciation: [ˈvaɪmaɐ̯]; Latin: Vimaria or Vinaria) is a city in the federal state of Thuringia, Germany. It is located in Central Germany between Erfurt in the west and Jena in the east, approximately 80 kilometres (50 miles) southwest of Leipzig, 170 kilometres (106 miles) north of Nuremberg and 170 kilometres (106 miles) west of Dresden. Together with the neighbour-cities Erfurt and Jena it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 inhabitants, whereas the city itself counts a population of 65,000. Weimar is well known because of its large cultural heritage and its importance in German history.
The city was a focal point of the German Enlightenment and home of the leading personalities of the literary genre of Weimar Classicism, the writers Johann Wolfgang von Goethe and Friedrich Schiller. In the 19th century, famous composers like Franz Liszt made Weimar a music centre and later, artists and architects like Henry van de Velde, Wassily Kandinsky, Paul Klee, Lyonel Feininger and Walter Gropius came to the city and founded the Bauhaus movement, the most important German design school of the interwar period. However, the political history of 20th-century Weimar was inconsistent: it was the place where Germany's first democratic constitution was signed after the First World War, giving its name to the Weimar Republic period in German politics (1918–33), as well as one of the cities mythologized by the National Socialist propaganda.
Until 1948, Weimar was the capital of Thuringia. Today, many places in the city centre have been designated as UNESCO World Heritage sites (either as part of the Weimar Classicism complex or as part of the Bauhaus complex) and tourism is one of the leading economic sectors of Weimar. Relevant institutions in Weimar are the Bauhaus University, the Liszt School of Music, the Duchess Anna Amalia Library and two leading courts of Thuringia (the Supreme Administrative Court and Constitutional Court).
Other: Thuringia, Eichsfeld, Kyffhäuserkreis, Schmalkalden-Meiningen, Sömmerda, Landkreis Saalfeld-Rudolstadt, Saale-Orla-Kreis, Greiz, Altenburger Land, Eisenach, Wartburgkreis, Erfurt, Gera, Saale-Holzland-Kreis, Ilm-Kreis, Suhl, Sonneberg, Unstrut-Hainich-Kreis, Jena, Hildburghausen, Weimarer Land, Nordhausen, Weimar, Gotha
Neighbours: Weimarer Land
Suggested citation: Michal Páleník: Europe and its regions in numbers - Weimar – DEG05, IZ Bratislava, retrieved from: https://www.iz.sk/PDEG05, ISBN: 978-80-970204-9-1, DOI:10.5281/zenodo.10200164

 Share
Share Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter News
News