- About us»
- Net income calculator»
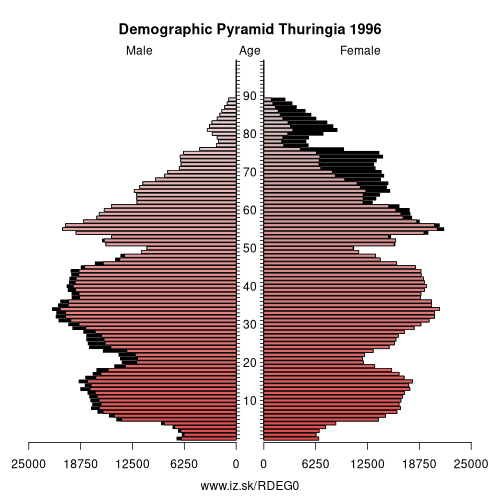
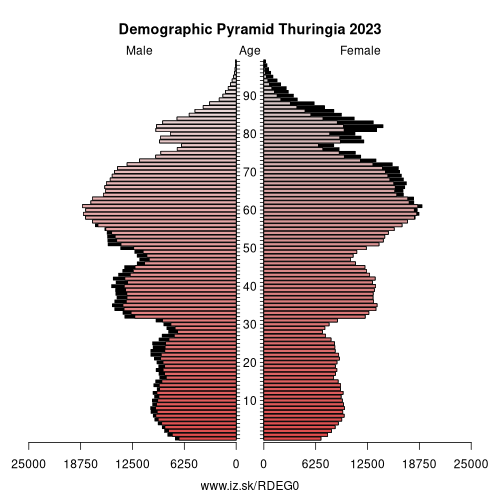
- Population aging»
-
-
- Unemployment structure in the Visegrad region
- Development in least developed regions
- Detailed statistics of least developed regions in Slovakia
- Statistics of the least developed regions in Slovakia
-
- Average wage
- Material need benefits
- Meal allowance
- Counties of Slovakia
- Inflation
- Living and Subsistence Minimum
- Unemployment of Czechia and Slovakia
- NACE Classification
-
- Life expectancy
- Gender differences
- Youth unemployment and NEET
- Minimum wage in EU
- Unemployment rates of different age groups
- Share of salaries on GDP
- Unemployment rate
- Percentage of employees ususally working at nights
- Employment rate
- NEET
- Long term unemployment
-
- Bratislava and surroundings
- Kopanice
- Danube river
- lower Vah river
- middle Vár river
- upper Nitra river
- lower Nitra river
- Mining cities
- Kysuce a Orava
- upper Vah river - Liptov
- Spiš cities
- upper Hron river
- Juhoslovenská kotlina
- Košice fold and Torysa river
- upper Zemplín
- lower Zemplín
- EU regions
- NUTS3 regions of Slovakia
- LAU1 dataset
-
-
- Projects and activities
- Inclusive growth»
- Good work
- Project SKRS
- Social system – reality and vision
- Library
-
- Education of unemployed
- Young unemployed not taking part in education
- Proposal to change the system of education funding
- News»
- Contact
Thuringia – DEG0
EU regions: Germany > Thuringia > Thuringia
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Life long learning | ||
| life long learning participation | 2024 | 7.8 |
| Part time jobs and flexible employment | ||
| percentage of part time workers | 2024 | 24.86 |
| percentage of part time workers, men | 2024 | 11.1 |
| percentage of part time workers, women | 2024 | 40.62 |
| Gender differences | ||
| gender gap in employment rate | 2024 | 94.21 |
| gender gap in unemployment rate | 2024 | 91.67 |
| Graduates and young people | ||
| unemployment rate of youth with elementary education | 2008 | 11 |
| NEET | 2024 | 8.8 |
| Gross domestic product | ||
| GDP per capita in PPS of EU average | 2024 | 83 |
| Employment | ||
| employment rate | 2024 | 77.2 |
| Social exclusion | ||
| people at risk of poverty or social exclusion | 2019 | 19.3 |
Thuringia slovensky: DEG0
Subregions: Erfurt, Gera, Jena, Suhl, Weimar, Eichsfeld, Nordhausen, Unstrut-Hainich-Kreis, Kyffhäuserkreis, Schmalkalden-Meiningen, Gotha, Sömmerda, Hildburghausen, Ilm-Kreis, Weimarer Land, Sonneberg, Landkreis Saalfeld-Rudolstadt, Saale-Holzland-Kreis, Saale-Orla-Kreis, Greiz, Altenburger Land, Eisenach, Wartburgkreis
Unemployment
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Unemployment | ||
| unemployment rate | 2024 | 3.6 |
| youth unemployment rate | 2019 | 7.7 |
| Long term unemployment | ||
| long term unemployment | 2024 | 1.2 |
| share of long term unemployed | 2024 | 34.6 |
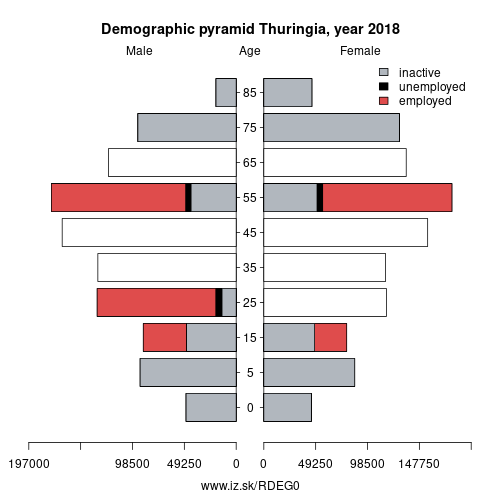
Demographics
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||
| number of inhabitants | 2025 | 2 100 277 |
| population density | 2023 | 131.4 |
| old-age dependency ratio | 2025 | 47.2 |
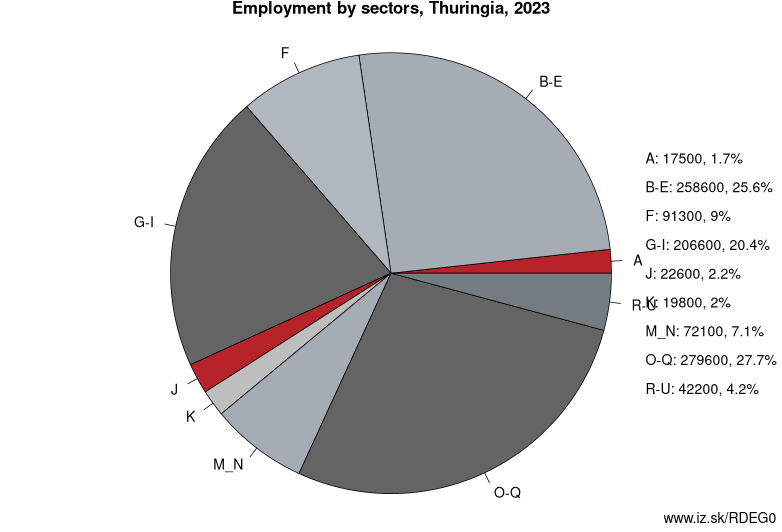
Employment by sectors, Thuringia
| NACE r2 | % | NACE r2 | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 15.3 | 2% | B-E | 231.3 | 23% |
| F | 81.2 | 8% | G-I | 206.6 | 21% |
| J | 27.5 | 3% | K | 18.8 | 2% |
| M_N | 76.1 | 8% | O-Q | 293.8 | 29% |
| R-U | 46.3 | 5% | TOTAL | 1006 | 100% |
Data for the period year 2024. Source of the data is Eurostat, table [lfst_r_lfe2en2].
From Wikipedia : Thuringia (German: Thüringen) (German pronunciation: [ˈtyːʁɪŋən] (listen)), officially the Free State of Thuringia (English: ; German: Freistaat Thüringen, pronounced [ˈfʁaɪʃtaːt ˈtyːʁɪŋən]), is a state of Germany.
Thuringia is located in central Germany covering an area of 16,171 square kilometres (6,244 sq mi) and a population of 2.15 million inhabitants, making it the sixth smallest German state by area and the fifth smallest by population. Erfurt is the state capital and largest city, while other major cities include Jena, Gera, and Weimar. Thuringia is surrounded by the states of Bavaria, Hesse, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony.
Most of Thuringia is within the watershed of the Saale, a left tributary of the Elbe, and has been known as „the green heart of Germany" (das grüne Herz Deutschlands) from the late 19th century due to the dense forest covering the land. Thuringia is home to the Rennsteig, Germany's most well-known hiking trail, and the winter resort of Oberhof, making it a well-known winter sports destination with half of Germany's 136 Winter Olympic gold medals won through 2014 having been won by Thuringian athletes. Thuringia is also home to prominent German intellectuals and creative artists, including Johann Sebastian Bach, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, and Friedrich Schiller, and is location of the University of Jena, the Ilmenau University of Technology, the University of Erfurt, and the Bauhaus University of Weimar.
Thuringia was established in 1920 as a state of the Weimar Republic from a merger of the Ernestine duchies, except for Saxe-Coburg, but can trace its origins to the Frankish Duchy of Thuringia established around 631 AD by King Dagobert I. After World War II, Thuringia came under the Soviet occupation zone in Allied-occupied Germany, and its borders altered to become contiguous. Thuringia became part of the German Democratic Republic in 1949, but was dissolved in 1952 during administrative reforms, and its territory divided into the districts of Erfurt, Suhl and Gera. Thuringia was re-established in 1990 following German reunification, with slightly different borders, and became one of the Federal Republic of Germany's new states.
Neighbours: Brunswick Government Region, Saxony-Anhalt, Leipzig Government Region, Lower Franconia, Kassel Government Region, Chemnitz Government Region, Upper Franconia
Subregions: Erfurt, Gera, Jena, Suhl, Weimar, Eichsfeld, Nordhausen, Unstrut-Hainich-Kreis, Kyffhäuserkreis, Schmalkalden-Meiningen, Gotha, Sömmerda, Hildburghausen, Ilm-Kreis, Weimarer Land, Sonneberg, Landkreis Saalfeld-Rudolstadt, Saale-Holzland-Kreis, Saale-Orla-Kreis, Greiz, Altenburger Land, Eisenach, Wartburgkreis
Suggested citation: Michal Páleník: Europe and its regions in numbers - Thuringia – DEG0, IZ Bratislava, retrieved from: https://www.iz.sk/PDEG0, ISBN: 978-80-970204-9-1, DOI:10.5281/zenodo.10200164

 Share
Share Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter News
News