- About us»
- Net income calculator»
- Population aging»
-
-
- Unemployment structure in the Visegrad region
- Development in least developed regions
- Detailed statistics of least developed regions in Slovakia
- Statistics of the least developed regions in Slovakia
-
- Average wage
- Material need benefits
- Meal allowance
- Counties of Slovakia
- Inflation
- Living and Subsistence Minimum
- Unemployment of Czechia and Slovakia
- NACE Classification
-
- Life expectancy
- Gender differences
- Youth unemployment and NEET
- Minimum wage in EU
- Unemployment rates of different age groups
- Share of salaries on GDP
- Long term unemployment
- NEET
- Unemployment rate
- Percentage of employees ususally working at nights
- Employment rate
-
- Bratislava and surroundings
- Kopanice
- Danube river
- lower Vah river
- middle Vár river
- upper Nitra river
- lower Nitra river
- Mining cities
- Kysuce a Orava
- upper Vah river - Liptov
- Spiš cities
- upper Hron river
- Juhoslovenská kotlina
- Košice fold and Torysa river
- upper Zemplín
- lower Zemplín
- EU regions
- NUTS3 regions of Slovakia
- LAU1 dataset
-
-
- Projects and activities
- Inclusive growth»
- Good work
- Project SKRS
- Social system – reality and vision
- Library
-
- Education of unemployed
- Young unemployed not taking part in education
- Proposal to change the system of education funding
- News»
- Contact
Emilia-Romagna – ITH5
EU regions: Italy > Northeast Italy > Emilia-Romagna
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Life long learning | ||
| life long learning participation | 2024 | 13.6 |
| Part time jobs and flexible employment | ||
| percentage of part time workers | 2024 | 15.91 |
| percentage of part time workers, men | 2024 | 5.97 |
| percentage of part time workers, women | 2024 | 28.1 |
| Gender differences | ||
| gender gap in employment rate | 2024 | 81.65 |
| gender gap in unemployment rate | 2024 | 158.82 |
| Graduates and young people | ||
| unemployment rate of youth with elementary education | 2024 | 19.7 |
| NEET | 2024 | 7.4 |
| Gross domestic product | ||
| GDP per capita in PPS of EU average | 2024 | 117 |
| Employment | ||
| employment rate | 2024 | 70.3 |
| Social exclusion | ||
| people at risk of poverty or social exclusion | 2020 | 11 |
Emilia-Romagna slovensky: ITH5
Subregions: Province of Piacenza, Province of Parma, Province of Reggio Emilia, Province of Modena, Province of Bologna, Province of Ferrara, Province of Ravenna, Province of Forlì-Cesena, Province of Rimini
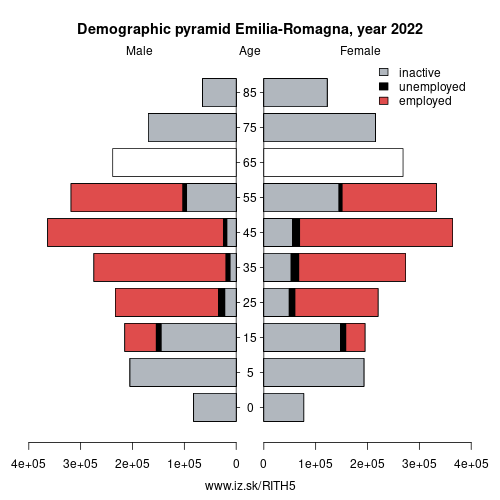
Unemployment
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Unemployment | ||
| unemployment rate | 2024 | 4.4 |
| youth unemployment rate | 2024 | 12.3 |
| Long term unemployment | ||
| long term unemployment | 2024 | 1.4 |
| share of long term unemployed | 2024 | 33.4 |
Demographics
| Indicator | Period | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||
| number of inhabitants | 2025 | 4 461 998 |
| population density | 2023 | 200.7 |
| old-age dependency ratio | 2025 | 39.4 |
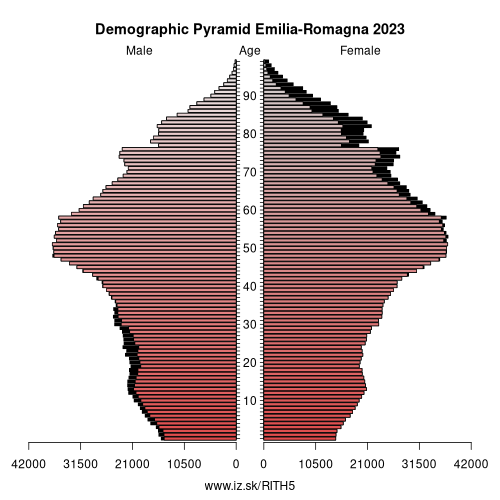
Employment by sectors, Emilia-Romagna
| NACE r2 | % | NACE r2 | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 65.4 | 3% | B-E | 555.2 | 27% |
| F | 112.8 | 6% | G-I | 501.6 | 25% |
| J | 55.1 | 3% | K | 53 | 3% |
| L | 10.1 | 0% | M_N | 193.9 | 10% |
| O-Q | 349.3 | 17% | R-U | 136.3 | 7% |
| TOTAL | 2032.6 | 100% |
Data for the period year 2024. Source of the data is Eurostat, table [lfst_r_lfe2en2].
From Wikipedia : Emilia-Romagna (UK: , US: , both also ; Italian: [eˈmiːlja roˈmaɲɲa]; Emilian and Romagnol: Emélia-Rumâgna) is an administrative region of Northeast Italy comprising the historical regions of Emilia and Romagna. Its capital is Bologna. It has an area of 22,446 km2 (8,666 sq mi), and about 4.4 million inhabitants.
Emilia-Romagna is one of the wealthiest and most developed regions in Europe, with the third highest GDP per capita in Italy. Bologna, its capital, has one of Italy's highest quality of life indices and advanced social services. Emilia-Romagna is also a cultural and tourist centre, being the home of the University of Bologna, the oldest university in the world, containing Romanesque and Renaissance cities (such as Modena, Parma and Ferrara), a former Eastern Roman Empire capital such as Ravenna, encompassing eleven UNESCO heritage sites, being a centre for food and automobile production (home of automotive companies such as Ferrari, Lamborghini, Maserati, Pagani, De Tomaso and Ducati) and having popular coastal resorts such as Cervia, Cesenatico, Rimini and Riccione.
In 2018, the Lonely Planet guide named Emilia Romagna as the best place to see in Europe.Etymology
The name Emilia-Romagna is a legacy of Ancient Rome. Emilia derives from the via Aemilia, the Roman road connecting Piacenza to Rimini, completed in 187 BC and named after the consul Marcus Aemilius Lepidus. Romagna derives from Romània, the name of the Eastern Roman Empire applied to Ravenna by the Lombards when the western Empire had ceased to exist and Ravenna was an outpost of the east (540–751).
History
Before the Romans took control of present-day Emilia-Romagna, it had been part of the Etruscan world and then that of the Gauls.
Other: Northeast Italy, Emilia-Romagna, Trentino-South Tyrol, South Tyrol, Veneto, Friuli Venezia Giulia
Neighbours: Veneto, Piedmont, Tuscany, Marche, Lombardy, Liguria
Subregions: Province of Piacenza, Province of Parma, Province of Reggio Emilia, Province of Modena, Province of Bologna, Province of Ferrara, Province of Ravenna, Province of Forlì-Cesena, Province of Rimini
Suggested citation: Michal Páleník: Europe and its regions in numbers - Emilia-Romagna – ITH5, IZ Bratislava, retrieved from: https://www.iz.sk/PITH5, ISBN: 978-80-970204-9-1, DOI:10.5281/zenodo.10200164

 Share
Share Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter News
News